Home »
Popular Posts
Leaky Gut Syndrome: Science, Symptoms & Solutions
Naturopathic Physicians have been diagnosing Leaky Gut Syndrome for decades, in their quest for treating the cause(s) in patients suffering from indigestion, allergies, hormonal imbalance, brain, skin & autoimmune diseases. Only recently has this condition become more mainstream as scientists are investigating the profound link between Leaky Gut Syndrome and various chronic diseases. Much of our North American population unknowingly struggles with leaky gut given our society’s poor diet, toxic exposures and chronic stress. Although a century of documentation exists, Medical Doctors are finally acknowledging the validity of this affliction.
Leaky Gut Affects Your Whole Body
You would think that Leaky Gut Syndrome would target digestive function only. In fact, Leaky Gut Syndrome is the cause for many severe & chronic health conditions, as bowel health determines overall health. This has been since Hippocrates, who stated “All Disease Begins In The Gut”. We review the science, symptoms, causes and solutions for Leaky Gut Syndrome, so you can take charge of your health.
Science of Leaky Gut Syndrome
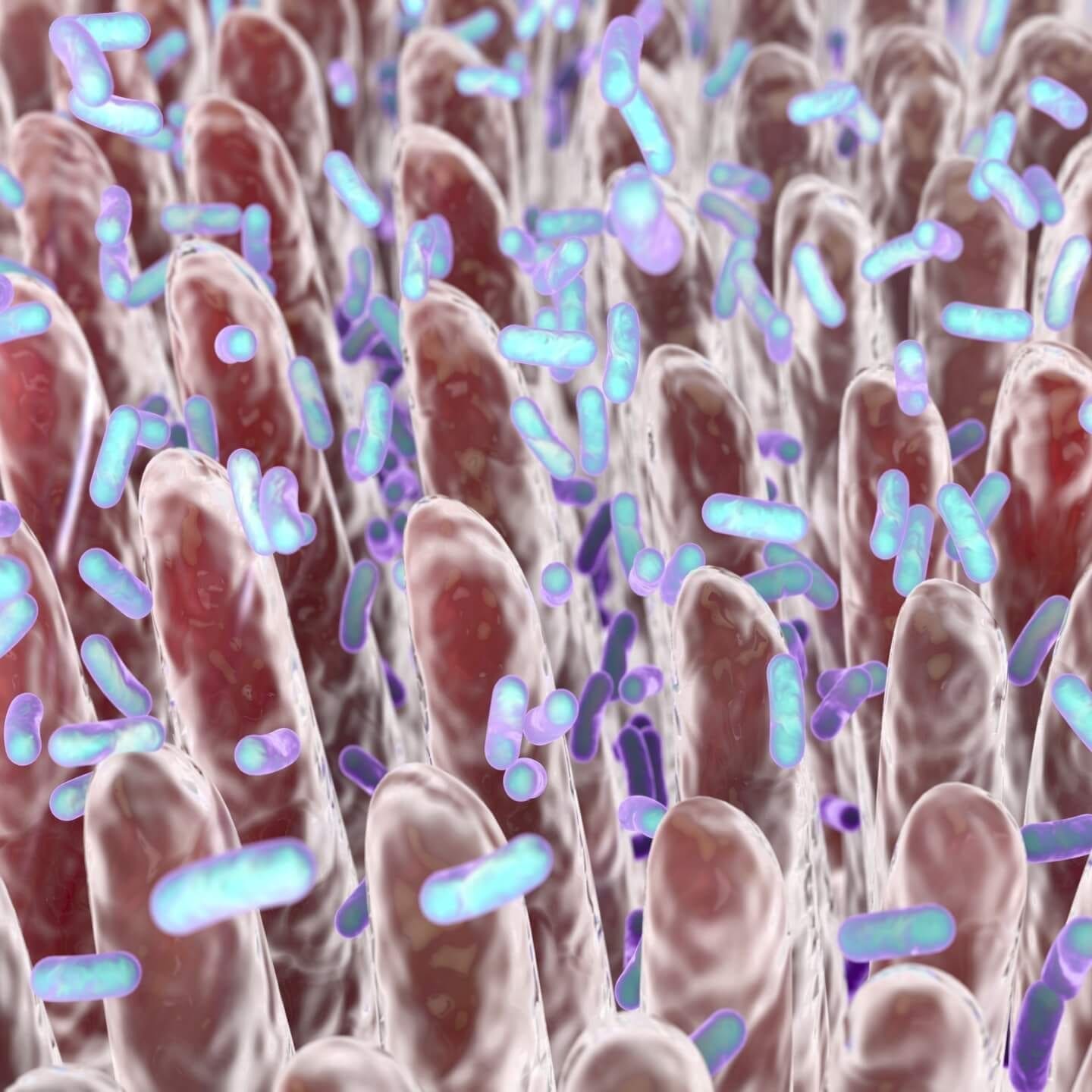
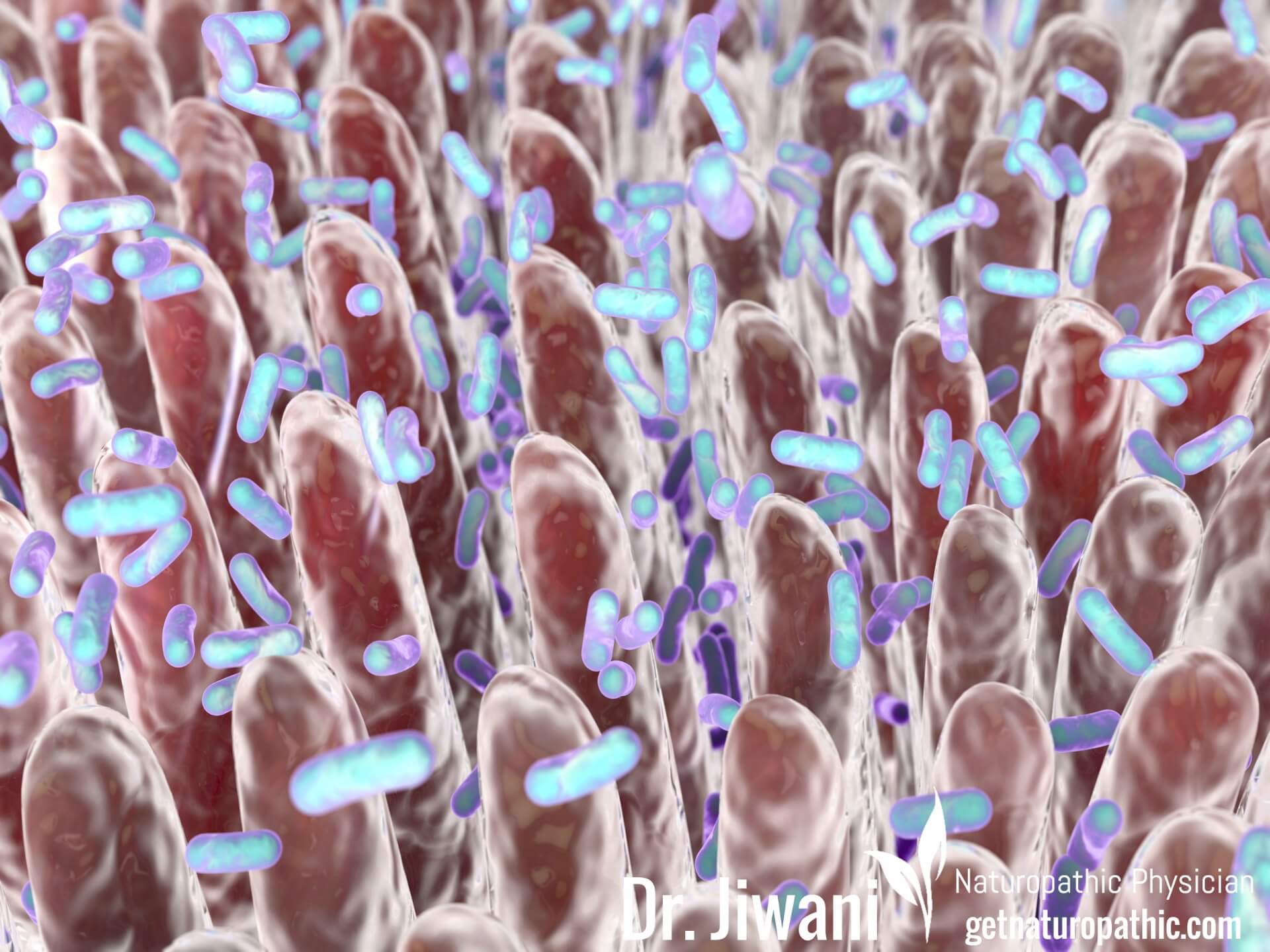
The intestines are a site for digestion and absorption of nutrients, to an acceptably small size. Imagine straining vegetable broth to keep out the large spices and chunks of vegetables. Your intestines have “tight junctions” that, like the size of the mesh in the sieve, allows only liquid or very small molecules to go through (permeability). The intestines have this protective barrier, which is the first line of defense in your immune system, to prevent bacteria, toxins and undigested food from attacking through the bowel.
Leaky Gut: Like Holes in a Wall
Leaky Gut Syndrome is scientifically termed as “increased intestinal permeability” or intestinal barrier dysfunction. This means that there are holes in the wall or damage to the intestines (tight junctions). This allows larger, undigested food particles, toxins and unwanted microbes to enter your system and break down your immunity.
Gut-Allergy-Yeast Connection
Proper immunity towards food relies on the intestinal permeability of the gut to regulate passage of nutrients and restrict larger molecules. This regulation relies on complex physical, chemical & immune mechanisms. In predisposed individuals, when food allergies develop they cause allergic reaction & inflammation damaging the gut lining, increasing intestinal permeability. This intestinal barrier dysfunction means more allergens enter through the leaky gut, triggering more inflammation, which perpetuates the vicious cycle including the development of more food allergies, per Perrier 2011.
Leaky Gut & Your Microbiome
Gut bacterial balance (microbiome) plays a critical role in regulating intestinal permeability per Kelly 2015. Negative microbiome changes can cause Leaky Gut Syndrome, and leads to overgrowth of bad bacteria, yeast & fungi which can enter the body through the leaky gut causing systemic yeast infection (Candidiasis) which itself can lead to the symptoms below.
Conditions Associated with Leaky Gut Syndrome
- Acne
- Autism, ADD, ADHD
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Asthma
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Celiac Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
- Depression
- Diabetes Type I
- Eczema
- Food Allergies
- Hashimoto’s Thyroid
- Irritable Bowel
- Kidney Disease
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms from Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky Gut Syndrome may also present with vague symptoms, such as:
- Anxiety, Depression
- Constipation, Diarrhea
- Candida / Fungal Infections
- Chronic Fatigue / Fibromyalgia
- Cravings for Sweets / Carbs
- Food Allergies / Sensitivities
- Gas, Bloating
- Headaches
- Heartburn / Reflux
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Joint Pain
- Nutrient Deficiencies
- Recurrent Infections
- Skin Diseases
- Thyroid Issues
- Weight Gain
Causes of Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky Gut Syndrome may be triggered by improper diet, toxins, bacterial imbalance & chronic stress.
Dietary Factors That Cause Leaky Gut Syndrome
Food Allergies
Food Allergies are associated with increased intestinal permeability in studies since Barau 1990
Sugar
Sugar feeds yeast (Candida), bad bacteria & parasites that can overpower your good bacteria causing an unhealthy bowel environment (dysbiosis). The toxins produced from dysbiosis triggers inflammation which leads to changes in intestinal permeability (Leaky Gut Syndrome) & autoimmune diseases per Brown 2012.
Alcohol
Alcohol adds yeast into your system leading to dysbiosis & leaky gut. Leclercq 2014 confirmed that “gut microbiota could alter the gut-barrier function and influence behaviour in alcohol dependence”.
Caffeine
Other than overstimulating acidity in the stomach, caffeine looks similar to gluten so your body may also react to coffee proteins if you are allergic to gluten.
Gluten
Gluten is a protein in grains that degrades your gut lining. Arrieta 2006 discusses the damaging role of gluten in leaky gut syndrome.
Dairy
Cow’s milk & products contain the protein casein which inflames your gut as pasteurization destroys enzymes, making the lactose sugar hard to digest.
Genetically Modified Foods
Scientifically altered to resist bugs, genetically modified organisms (GMO) concentrate the lectins in these foods, making them more damaging to your gut.
Unsprouted Grains
Unsprouted grains are high in phytates and lectin proteins, which damage intestinal lining through inflammation. This can cause Leaky Gut Syndrome and autoimmune disease in those predisposed.
Toxins
We are exposed to thousands of chemicals & toxins through Pesticides, Antibiotics, Tap Water, NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) like Ibuprofen (Advil), Chemotherapy, Radiation. These toxins act like fire to scorch your intestinal lining leading to Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Bowel Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis is an unhealthy bowel environment which occurs with an imbalance of bad guys versus good guys. Certain factors cause this negative microbiome, as increased yeast, bad bacteria & parasites overpower your good bacteria. The toxins produced from dysbiosis triggers inflammation which leads to changes in intestinal permeability (Leaky Gut Syndrome) and autoimmune diseases in those genetically predisposed.
Elements That Provoke Bowel Dysbiosis Include:
- Antibiotics
- Psychological Stress
- High Sugar / Carb Diet
- Sulfites (Preservatives, Dried Fruits, Dehydrated Vegetables, Shellfish, Fruit Juices, Baked Goods, White Bread, Alcohol)
- Overgrowth of Yeast, Fungi, Parasites & Toxic Bacteria
Stress & Leaky Gut
Stress has a dramatic effect on your overall system by weakening immunity and increasing vulnerability to infection from bacteria, yeast (fungi), viruses & parasites. The profound impact on the gut is evident by changes in movements, secretions & intestinal permeability, reducing its healing ability, dysbiosis and causing chronic inflammation leading to Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Solutions to Healing Leaky Gut Syndrome
The key to addressing your leaky gut is a combination of treating the cause(s) and healing the existing damage. It is critical to understand that just popping pills will not rectify possibly decades of damage. It is just as important to change your diet as it is to supplement for optimal restoration of your intestinal permeability.
Address Dietary Issues
- Avoid Your Food Allergies
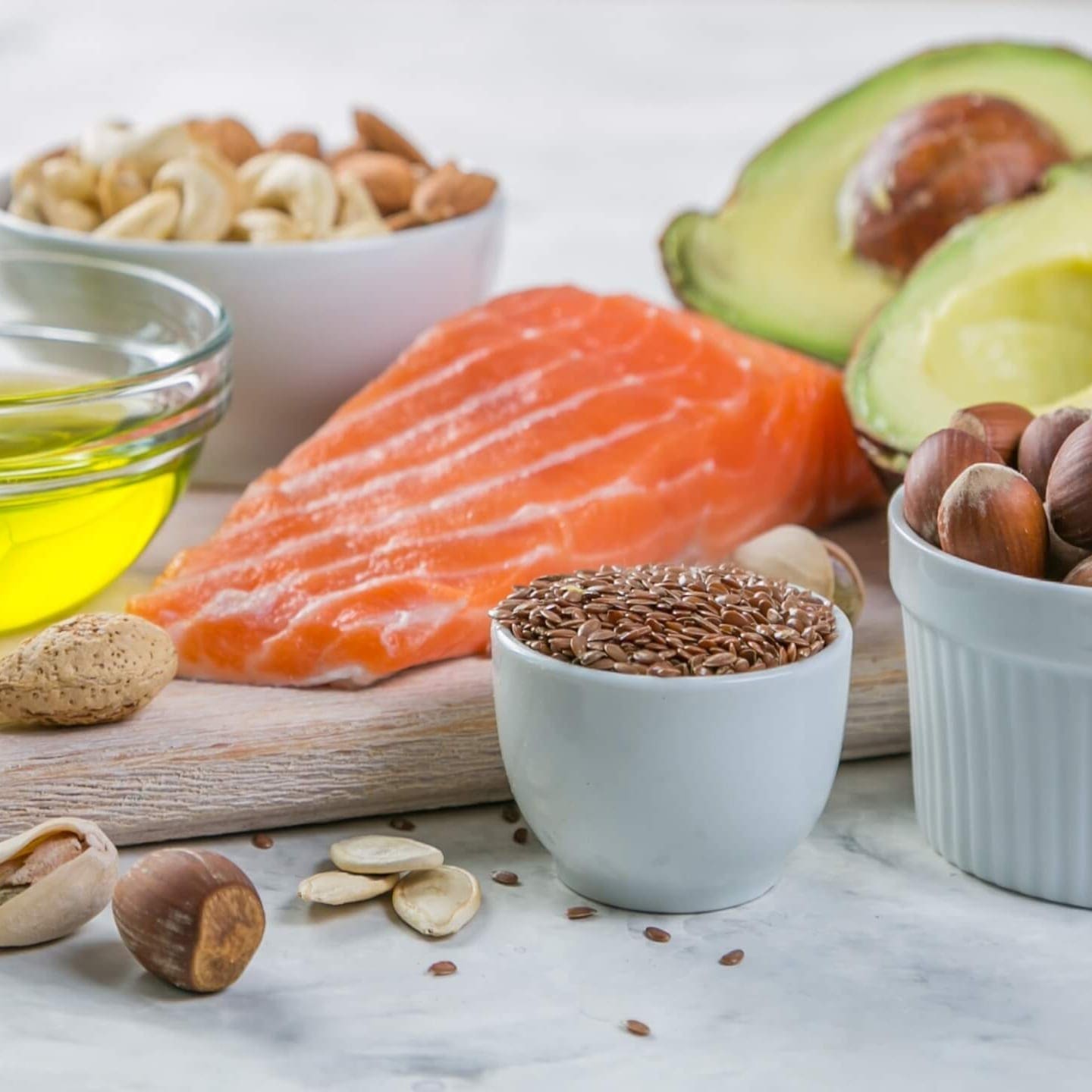
- Increase Good Fats: Avocado, Coconut Oil, Nuts, Seeds, Hemp Oil, Flax Oil
- Avoid Trans “Bad” Fats: Fried Foods, Margarine, Vegetable Oils
- Focus on Organic & NON-GMO Foods
- Drink Filtered Water
- Avoid Caffeine, Alcohol & Artificial Sweeteners
- Avoid Sugar & Excess Carbs: Use Healthier Sweeteners & Recipes: Coconut Sugar, Stevia, Xylitol
- Balance Carbs with Protein to Stabilize Blood Sugar
- Focus on Healthful Foods Specific to You
Balance Bowel Environment for Optimal Health
Probiotics are various forms of good bacteria, necessary to rebalance the bowel environment, by overpowering the bad guys (bad bacteria, yeast, parasites). Probiotics are essential for treating Leaky Gut Syndrome, as research has shown its prominent role in gut, brain and bowel health, and many conditions as above.
Supplements to Restore Healthy Gut Function
Turmeric (Curcumin) powerful inflammation modulator to assist in normalizing gut health & function Rapin 2010
Quercitin improves gut barrier, minimizes histamine release (allergic reactions)
L-Glutamine growth & repair of intestinal cells, supports immunity during stress Rapin 2010
N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (NADG) protects and restores a healthy mucosal layer, healthy immune modulation
Acacia senegal FibregumTM supports the growth of good bacteria & intestinal cell function
Vitamin A (All trans Beta-Carotene) maintain mucous membranes & healthy immune function
Digestive Enzymes minimizes large, undigested particles of food escaping into the blood stream, causing food allergies & the resulting inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining
Probiotics research has shown its prominent role in gut, brain and bowel health, good bacteria rebalances bowel environment by overpowering the bad guys – bad bacteria, yeast, parasites. Rosenfeldt 2004, Hulston 2015
Yeast Killer promotes good bacteria balance in those with unhealthy diets, history of chronic antibiotic use, or overgrowth of disease-causing microbes including Clostridium difficile, Helicobacter pylori or Candida albicans, anti-fungal effect for systemic yeast infections (candidiasis), 2000% stronger than common anti-fungal agent (caprylic acid)
Related Food Allergies: When Friend Becomes Foe
References
Anders HJ, Andersen K, Stecher B. The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney international. 2013 Jun 1;83(6):1010-6.
Arrieta MC, Bistritz L, Meddings JB. Alterations in intestinal permeability. Gut. 2006 Oct 1;55(10):1512-20.
Barau E, Dupont C. Modifications of intestinal permeability during food provocation procedures in pediatric irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 1990 Jul 1;11(1):72-7.
Benard A, Desreumeaux P, Huglo D, Hoorelbeke A, Tonnel AB, Wallaert B. Increased intestinal permeability in bronchial asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1996 Jun 30;97(6):1173-8.
Brown K, DeCoffe D, Molcan E, Gibson DL. Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients. 2012 Aug 21;4(8):1095-119.
Campbell AW. Autoimmunity and the Gut. Autoimmune diseases. 2014 May 13;2014.
de Magistris L, Familiari V, Pascotto A, Sapone A, Frolli A, Iardino P, Carteni M, De Rosa M, Francavilla R, Riegler G, Militerni R. Alterations of the intestinal barrier in patients with autism spectrum disorders and in their first-degree relatives. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2010 Oct 1;51(4):418-24.
Fasano A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology. 2012 Feb 1;42(1):71-8.
Fasano A. Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2012 Jul 1;1258(1):25-33.
Hollander D. Intestinal permeability barrier in Crohn’s disease: the difficulty in shifting the paradigm. Digestive diseases and sciences. 2013 Jul 1;58(7):1827.
Hulston CJ, Churnside AA, Venables MC. Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects. British Journal of Nutrition. 2015 Feb 28;113(04):596-602.
Humbert P, Bidet A, Treffel P, Drobacheff C, Agache P. Intestinal permeability in patients with psoriasis. Journal of dermatological science. 1991 Jul 1;2(4):324-6.
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Hyland NP. Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2015 Oct 14;9:392.
Lauret E, Rodrigo L. Celiac disease and autoimmune-associated conditions. BioMed research international. 2013 Jul 24;2013.
Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Jamar F, Stärkel P, Windey K, Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F, Verbeke K, De Timary P. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2014 Oct 21;111(42):E4485-93.
Maes M, Mihaylova I, Leunis JC. Increased serum IgA and IgM against LPS of enterobacteria in chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS): indication for the involvement of gram-negative enterobacteria in the etiology of CFS and for the presence of an increased gut–intestinal permeability. Journal of affective disorders. 2007 Apr 30;99(1):237-40.
Maes M, Kubera M, Leunis JC, Berk M. Increased IgA and IgM responses against gut commensals in chronic depression: further evidence for increased bacterial translocation or leaky gut. Journal of affective disorders. 2012 Dec 1;141(1):55-62.
Marí-Bauset S, Zazpe I, Mari-Sanchis A, Llopis-González A, Morales-Suárez-Varela M. Evidence of the gluten-free and casein-free diet in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Journal of child neurology. 2014 Dec;29(12):1718-27.
Michielan A, D’Incà R. Intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis, clinical evaluation, and therapy of leaky gut. Mediators of inflammation. 2015 Oct 25;2015.
Myers SP. The causes of intestinal dysbiosis: a review. Altern Med Rev. 2004 Jun;9(2):180-97.
Patil AD. Link between hypothyroidism and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism. 2014 May;18(3):307.
Pedersen L, Parlar S, Kvist K, Whiteley P, Shattock P. Data mining the ScanBrit study of a gluten-and casein-free dietary intervention for children with autism spectrum disorders: behavioural and psychometric measures of dietary response. Nutritional neuroscience. 2014 Sep 1;17(5):207-13.
Pennesi CM, Klein LC. Effectiveness of the gluten-free, casein-free diet for children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: based on parental report. Nutritional neuroscience. 2012 Mar 1;15(2):85-91.
Perrier C, Corthesy B. Gut permeability and food allergies. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2011 Jan 1;41(1):20-8.
Rapin JR, Wiernsperger N. Possible links between intestinal permeablity and food processing: a potential therapeutic niche for glutamine. Clinics. 2010;65(6):635-43.
Rosenfeldt V, Benfeldt E, Valerius NH, Pærregaard A, Michaelsen KF. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and small intestinal permeability in children with atopic dermatitis. The Journal of pediatrics. 2004 Nov 30;145(5):612-6.
Santocchi E, Guiducci L, Fulceri F, Billeci L, Buzzigoli E, Apicella F, Calderoni S, Grossi E, Morales MA, Muratori F. Gut to brain interaction in Autism Spectrum Disorders: a randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC psychiatry. 2016 Jun 4;16(1):183.
Smith MD, Gibson RA, Brooks PM. Abnormal bowel permeability in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 1985;12(2):299-305.
Vaarala O. Leaking gut in type 1 diabetes. Current opinion in gastroenterology. 2008 Nov 1;24(6):701-6.
Whiteley P, Shattock P, Knivsberg AM, Seim A, Reichelt KL, Todd L, Carr K, Hooper M. Gluten-and casein-free dietary intervention for autism spectrum conditions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2012;6.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts