Home »
Popular Posts
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Ketosis for Optimal Health & Fat Burning
Naturopathic Nuggets about the Ketogenic Diet
- The Ketogenic Diet is a century old remedy for epilepsy, that is now proven neuroprotective, affecting other neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s Disease.
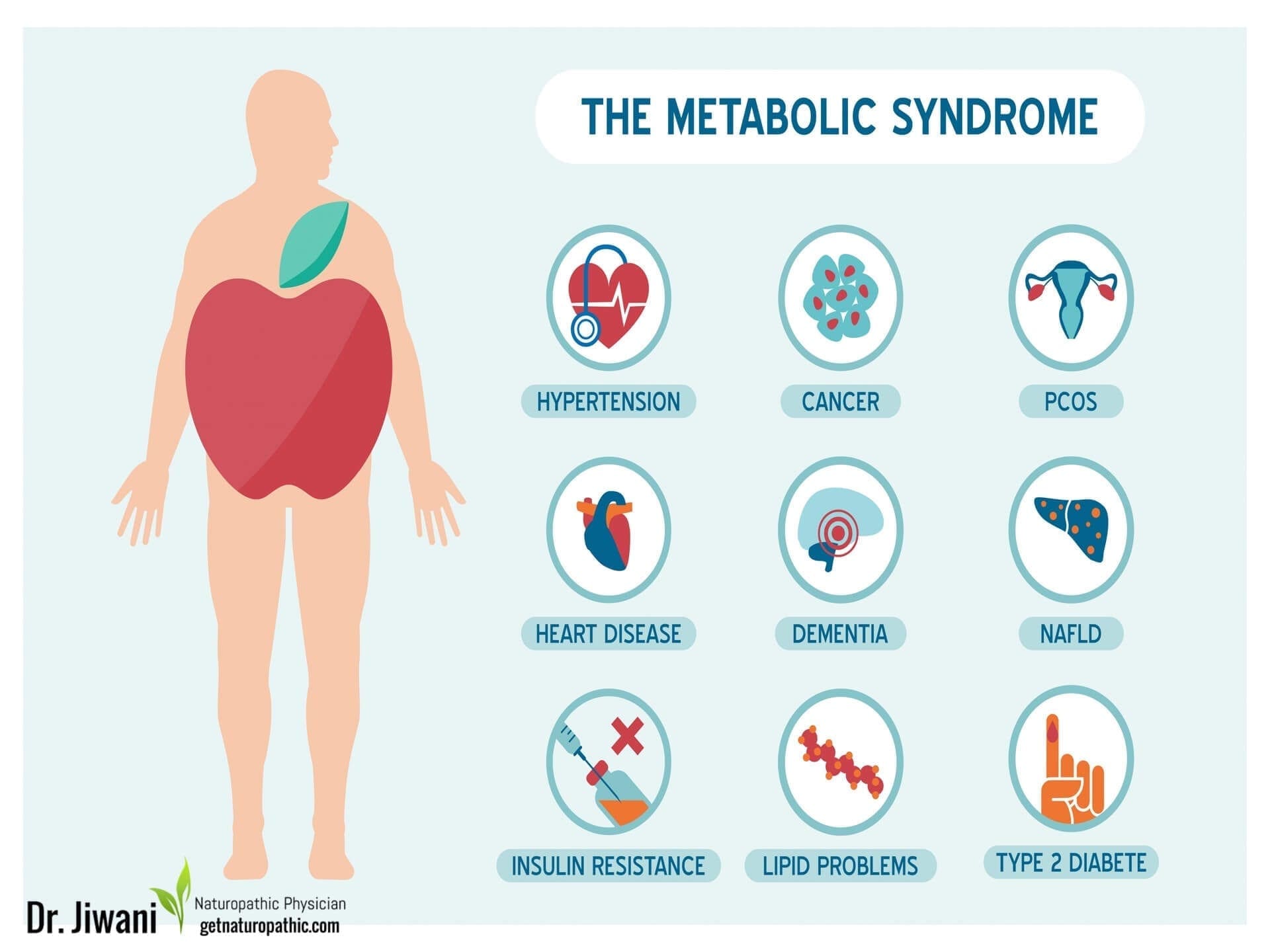
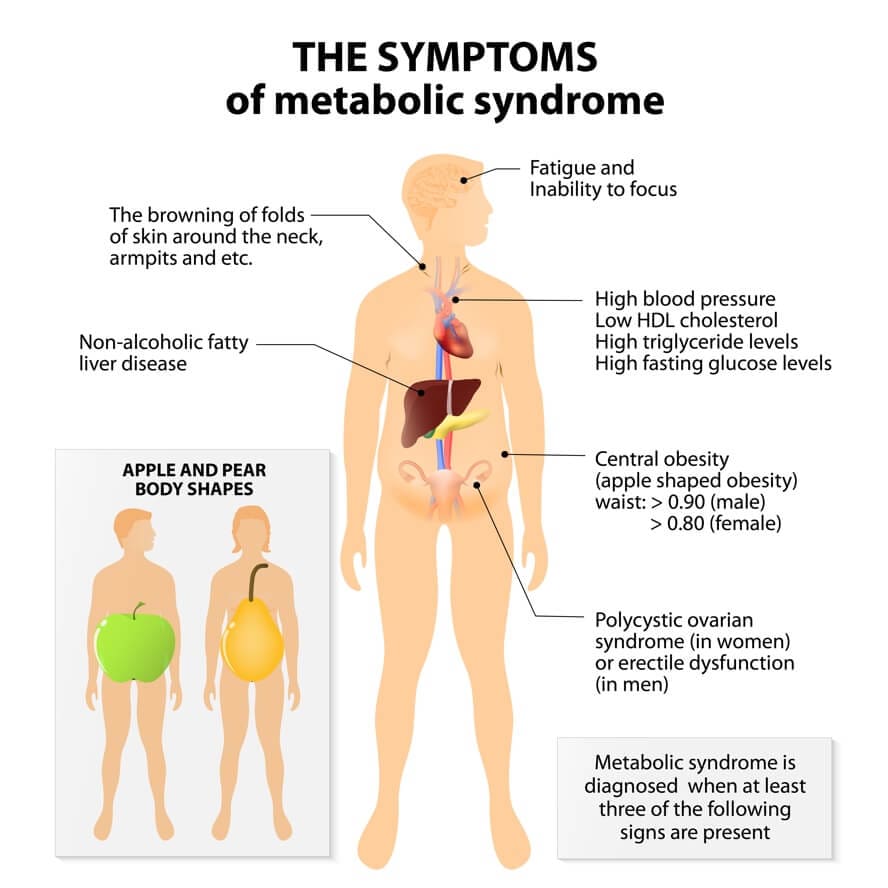
- The Ketogenic Diet has been researched to improve many conditions including Acne, Autoimmune Diseases, Cancer, Diabetes, Heart Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussions and Obesity
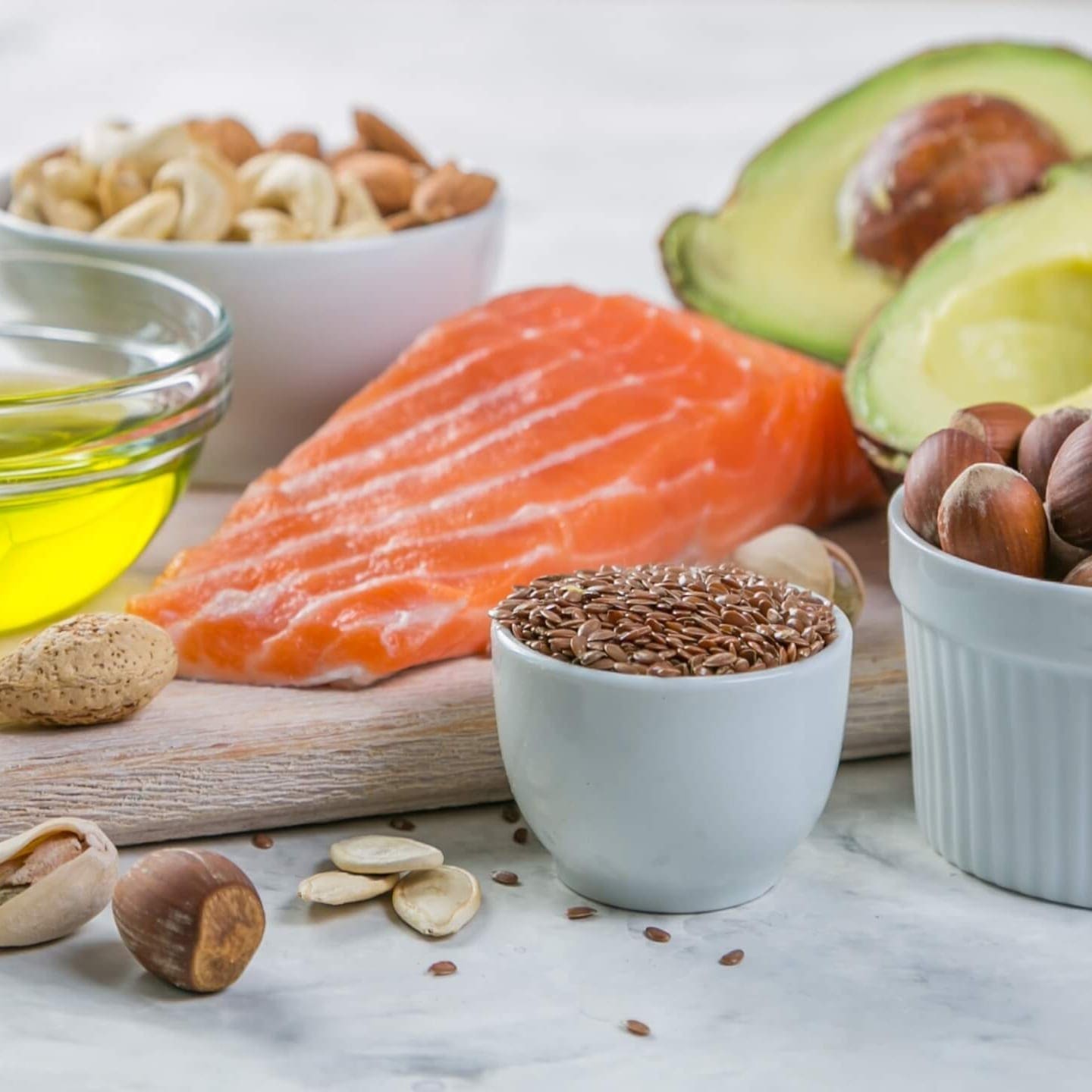
- A ketogenic diet consists of 70% healthy fats, 25% quality protein and 5% carbs to trigger ketosis for optimal fat burning and weight loss.
- To reach ketosis it is critical to avoid eating too many carbs or too much protein as either can become fuel for the body & brain. The key is to minimize carbs and increase fat to promote fat burning but prevent starvation which would cause muscle wasting.
- Side effects of ketosis include constipation, diarrhea, heart palpitations, keto breath, keto flu, leg cramps, reduced stamina & fitness. They are often the result of dehydration and/or salt deficiency, and usually resolve within a few weeks.
- Please consult your licensed Naturopathic Physician for assistance with the Ketogenic Diet if you suffer from diabetes, heart disease, gallbladder or pancreatic disease, or are taking prescription medications.
Ketogenic Diet: What is it?
A ketogenic diet is when carbs are dramatically reduced to 5% or less than 20 grams, protein is limited to 25%, and fat intake escalates to at least 70% to replace the carbs, helping you feel full. When carbs are restricted, the liver converts fat into ketones for energy & brain function. Instead of surviving on carbs (sugars) for brain fuel, your body uses ketones from your fat stores, transforming your body into an efficient fat-burning machine. This is called ketosis. In fact, many clinical studies have supported the countless benefits that a ketogenic diet has on health, weight loss and disease prevention.
The Ketogenic diet is different from the Atkins diet in that the ketogenic diet highlights less protein, no deli or processed meats (bacon & ham) and healthier fats. While both diets are low carb emphasizing the body’s fat-burning effect, the ketogenic diet has a lot of research to validate its effectiveness.
The ketogenic diet is now being studied for its neuroprotective effect through improved cellular metabolism on other neurological disorders aside from Epilepsy, including Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Autism, Brain Cancer, Headache, Neurotrauma (Traumatic Brain Injury), Pain, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Sleep Disorders (Gano, Patel, & Rho, 2014).
Ketogenic Diet: Why?
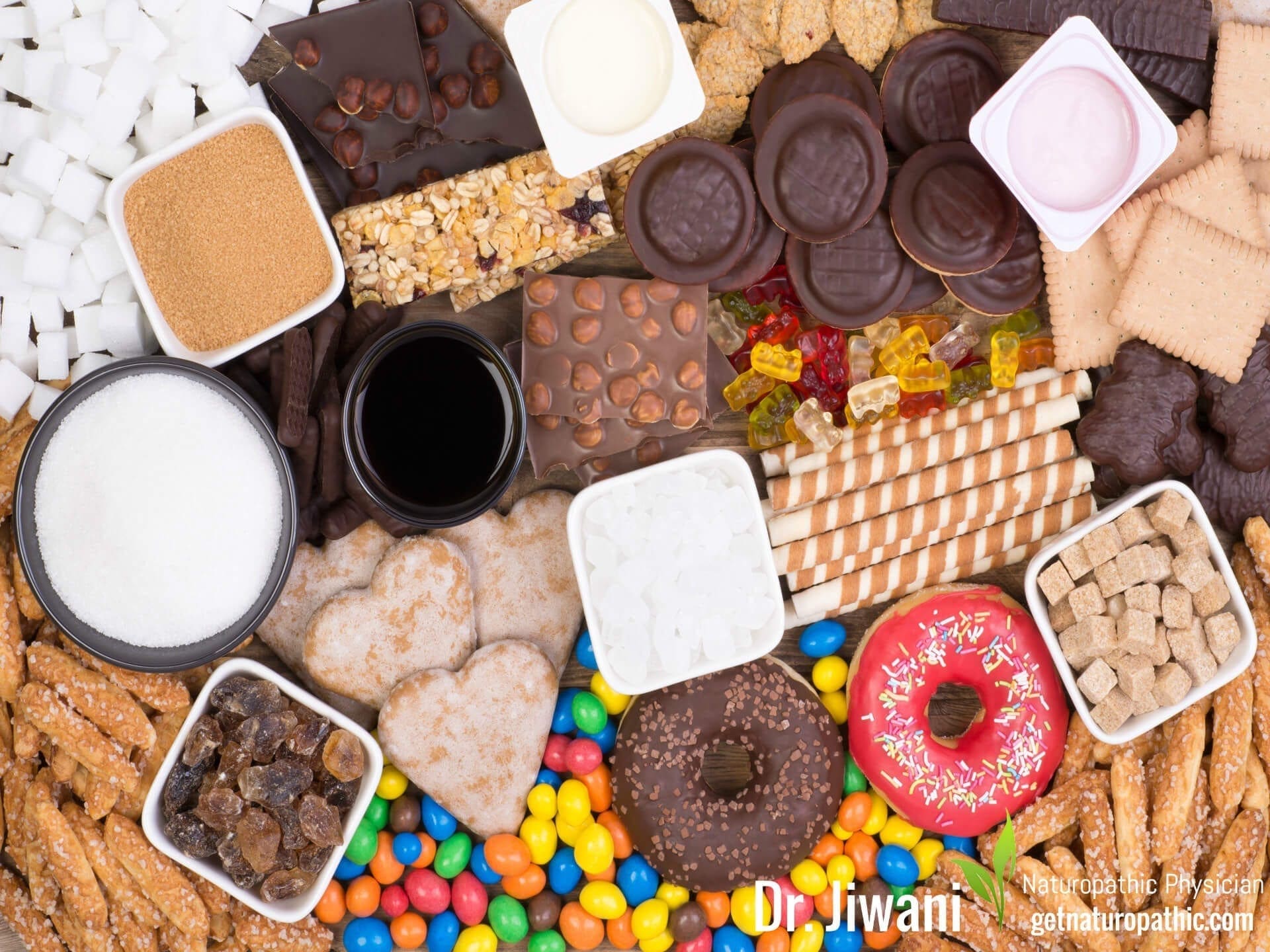
For many decades, the universally accepted diet in North America emphasized a high carbohydrate, low fat intake. However, recent studies verify this diet has backfired for the majority of North Americans.
Results from a long-term study by the Centres for Disease Control & Prevention indicate that in the last decade overweight North Americans have increased from ¼ to ⅓ of the population! As such, society is fatter and less healthy in view of all the health-related concerns associated with weight gain and nutrient deficiencies.
In fact, obesity is a growing epidemic worldwide, and increases risk for heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Ketogenic diets have proven to be highly effective in the fight against not only Obesity (Bueno et al., 2013), but also Diabetes, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Acne, Neurological Diseases, & Cancer while improving risk factors for Lung & Heart Disease (Paoli, Rubini, Volek, & Grimaldi, 2013).
The Keto Diet Health Benefits
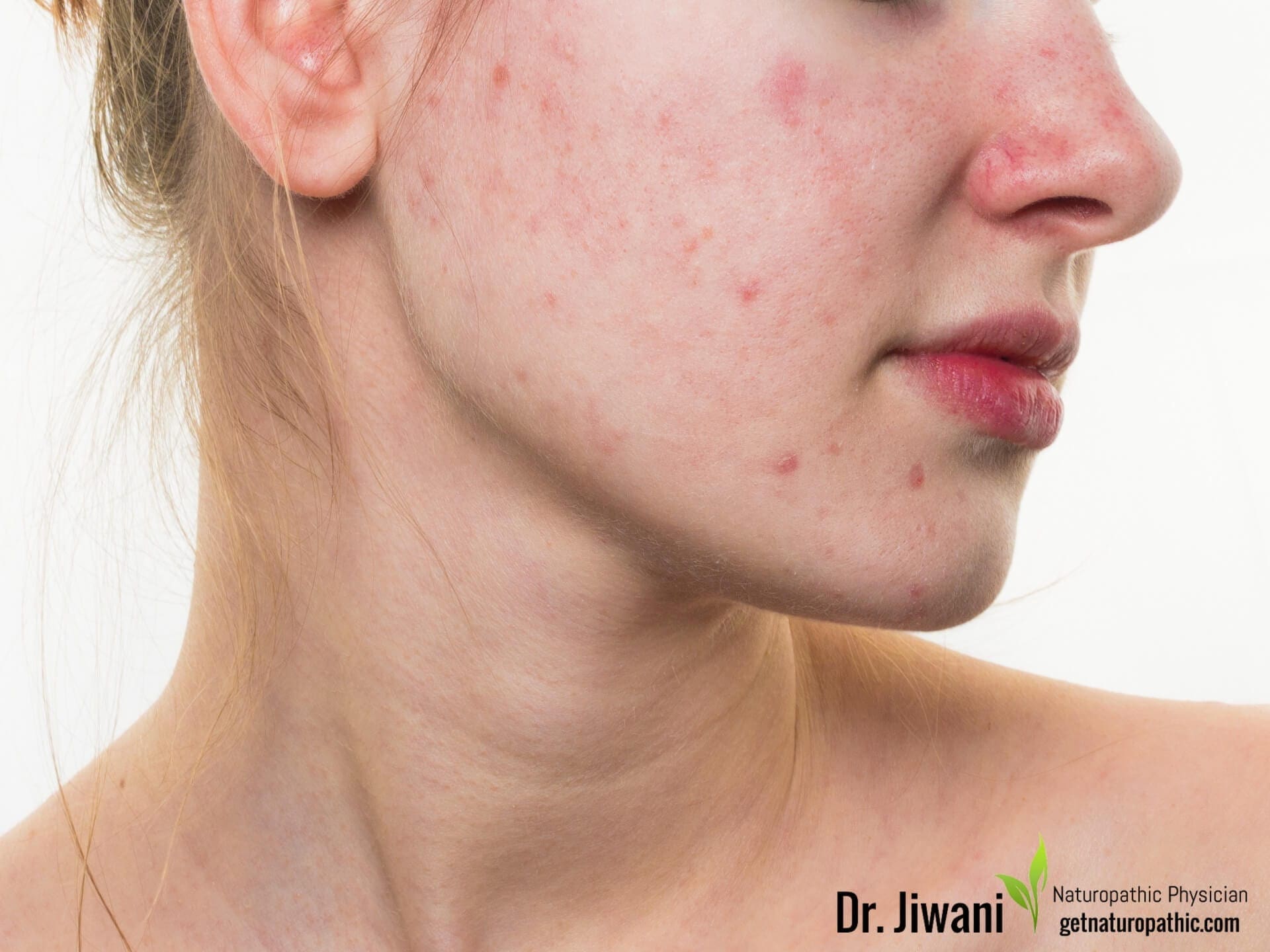
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Acne
Certain studies have proven that high carb diets may play a role in acne through stimulating insulin, increasing androgen bioavailability & influencing insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) activity. Ultimately, insulin mediated actions cause increased cell growth in sebaceous ducts, abnormal shedding of follicular skin, increased androgen-mediated sebum production, growth of acne bacteria and the consequent inflammation. Conversely, low carb diets improve skin quality (Smith, Mann, Braue, Mäkeläinen, & Varigos, 2007).
Clinical and physiological evidence has found that the ketogenic diet specifically may be effective in decreasing the severity and progression of acne (Paoli et al., 2012).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Alzheimer’s Disease
Recent research highlights the neuroprotective effects and even modify disease progression of the ketogenic diet on Alzheimer’s Disease and other neurodegenerative conditions (Gasior, Rogawski, & Hartman, 2006). In fact, Reger et al., 2004 administered medium chain fats and found improved memory in Alzheimer’s patients, and the degree of improvement matched the blood levels of ketones (β-hydroxybutyrate), which happens when the fat is converted to fuel.
Contrarily, high carb diets worsen cognitive performance & behaviour in Alzheimer’s patients (Young et al., 2005).
In fact, increasing essential fatty acids may be protective against Alzheimer’s Disease, while saturated or trans fats increase risk (Morris et al., 2003).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Appetite Regulation & Cravings
The ketogenic diet requires increased fat intake which helps you feel full. Meanwhile the ketones produced from fat conversion suppresses appetite and influences appetite control hormones. Ghrelin (hunger hormone) increases were suppressed & leptin was lower on the ketogenic diet (Sumithran et al., 2013). Basically, the ketogenic diet keeps you full and prevents rebound hunger causing weight regain.
A study actually found that obese adults on the low carb diet had dramatic reductions in carb & sugar cravings, and were less bothered by hunger compared to the low fat group (Martin et al., 2011).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Autoimmune Diseases
The mechanism of autoimmune diseases includes food allergies, which can cause gut & systemic inflammation, dysbiosis (altered gut bacteria) & leaky gut syndrome, all of which disrupt healthy immune function.
The ketogenic diet indirectly omits some food allergies through carbohydrate restriction, such as gluten, corn & rice grains, reducing inflammation. Ketosis also normalizes insulin function, which can fight inflammation as well. Additionally, the weight loss from a ketogenic diet can improve inflammation from fat cells.
A 2017 study in World Journal of Gastroenterology recognized the significant effect that a ketogenic diet had on an imbalanced gut microbiome. Microbial balance in epileptic infants was corrected with a ketogenic diet for one week, and 21% of infants became seizure-free, while others had a 50-90% reduction in seizure frequency (Xie et al., 2017).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Belly Fat (Visceral Fat)
A ketogenic diet not only causes weight loss but also fat loss, reducing inflammation which can perpetuate visceral obesity. A 2018 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, found that a ketogenic diet decreased fat mass and visceral adipose tissue without decreasing lean body mass (Vargas et al., 2018).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Cancer
Ketogenic diets have been researched to suppress tumour progression & systemic inflammation, while improving body & muscle weights in cancer cachexia, weight & muscle wasting (Nakamura, Tonouchi, Sasayama, & Ashida, 2018).
Cancer cells rely on glucose (sugar) for fuel. Ketogenic diets are used in cancer treatment to starve the cancer cells, as they cannot use ketones for fuel like healthy cells can. Moreover, reducing blood sugar reduces insulin & insulin-like growth factor, IGF-1, preventing cancer growth (Weber, Aminazdeh-Gohari, & Kofler, 2018).
Ketogenic diets have been found to increase survival time and slow tumour growth in pancreatic, prostate, stomach, brain & lung cancers (Khodadadi et al., 2017).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Cholesterol Imbalances (Low “Good” HDL & High “Bad” LDL)
Ketogenic diets have been associated with significant reductions in total cholesterol, increases in HDL “good” cholesterol levels, decreases in triglycerides “fat” levels and reductions in LDL “bad” cholesterol levels (Kosinski & Jornayvaz, 2017).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Diabetes Type 2
The effect of a ketogenic diet was investigated in type 2 diabetes patients versus a low glycemic diet. The ketogenic patients has greater improvements in their hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C), body weight and HDL “good” cholesterol compared to the low glycemic group. Stunningly, diabetic medications were reduced or eliminated in 95% of the ketogenic group. Clearly, ketogenic diets may be quite effective in improving and reversing type 2 diabetes (Westman, Yancy, Mavropoulos, Marquart, & McDuffie, 2008).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Epilepsy
Medically resistant epilepsy is very responsive to a ketogenic diet and has been used as a non-drug treatment since the 1920s. The proposed mechanisms include ketone production, low blood sugar, changes in brain energy metabolism, neuron cells, neurotransmitter function to improve the disease & reduce the seizure frequency (Agarwal et al., 2017).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Heart Disease
The ketogenic diet has been researched to improve all markers that define metabolic syndrome, including heart disease. A study in Lipids journal compared the low fat to the low carb diet with similar calorie intake. The ketogenic diet (low carb) was found to lower blood sugar & insulin levels, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce visceral fat & overall weight, while improving cholesterol profiles (less triglycerides, post-meal fat, ApoB ratio & Cholesterol/HDL ratio, with increased good cholesterol, HDL). Even though the ketogenic diet had 3X more dietary saturated fat, blood fats were reduced as was fat storing or lipogenesis (Volek et al., 2009).
Ketogenic diets have been associated with significant reductions in total cholesterol, increases in HDL “good” cholesterol levels, decreases in triglycerides “fat” levels and reductions in LDL “bad” cholesterol levels (Kosinski & Jornayvaz, 2017).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: High Blood Pressure
Studies for blood pressure are scarce. One study did find improvements in blood pressure in obese patients on a ketogenic diet over 48 weeks compared to a low fat diet (Mayer et al., 2014).
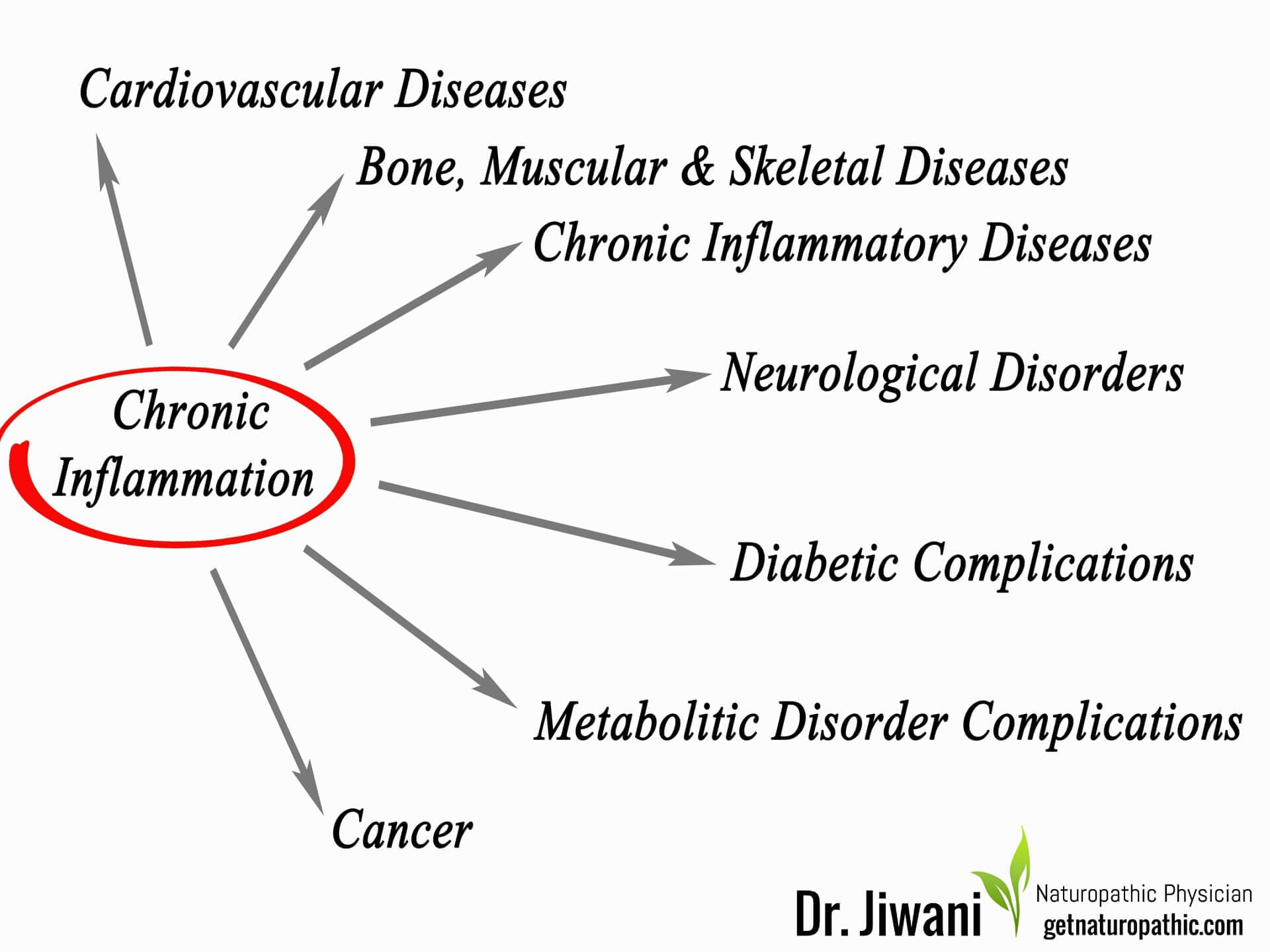
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Inflammation
Many studies support the anti-inflammatory benefits from ketogenic diets. It’s ability to reduce chronic inflammation enable the ketogenic diet to affect many conditions, including epilepsy, obesity, heart disease, autoimmunity, metabolic syndrome, and neurological diseases.(Pinto et al., 2018).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Insulin Resistance
The effect of a ketogenic diet was investigated in type 2 diabetes patients versus a low glycemic diet. The ketogenic patients has greater improvements in their hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C), body weight and HDL “good” cholesterol compared to the low glycemic group. Stunningly, diabetic medications were reduced or eliminated in 95% of the ketogenic group. Clearly, ketogenic diets may be quite effective in improving insulin resistance and reversing type 2 diabetes (Westman, Yancy, Mavropoulos, Marquart, & McDuffie, 2008).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Metabolic Syndrome
The ketogenic diet has been researched to improve all markers that define metabolic syndrome, including abdominal obesity, heart disease, high blood pressure, high blood sugar or insulin resistance and high blood fat. A study in Lipids journal compared the low fat to the low carb diet with similar calorie intake. The ketogenic diet (low carb) was found to lower blood sugar & insulin levels, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce visceral fat & overall weight, while improving cholesterol profiles (less triglycerides, post-meal fat, ApoB ratio & Cholesterol/HDL ratio, with increased good cholesterol, HDL). Even though the ketogenic diet had 3X more dietary saturated fat, blood fats were reduced as was fat storing or lipogenesis (Volek et al., 2009).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Muscle Gain
A ketogenic diet not only causes weight loss but also fat loss, reducing inflammation which can perpetuate visceral obesity. A 2018 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, found that a ketogenic diet decreased fat mass and visceral adipose tissue without decreasing lean body mass (Vargas et al., 2018).
Although ketogenic diets have shown increases in muscles mass while decreased fat in the obese & overweight, this was newly examined in resistance trained athletes, comparing a ketogenic diet to a traditional western diet (55 % carbs, 25 % fat, 20 % protein) on changes in muscle and fat mass. In fact, lean mass gain, muscle mass gain & fat loss was greater in the ketogenic group compared to the traditional western diet (Rauch et al., 2014).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Parkinson’s Disease
Although uncontrolled, one clinical study found 28 days on the ketogenic diet caused a 43% reduction in Parkinson’s symptoms. Also, all patients found moderate to very good improvement in symptoms (Vanitallie et al., 2005)
Similar to Alzheimer’s, increasing essential fatty acids was found to lower risk of developing Parkinson’s Disease (de Lau et al., 2005).
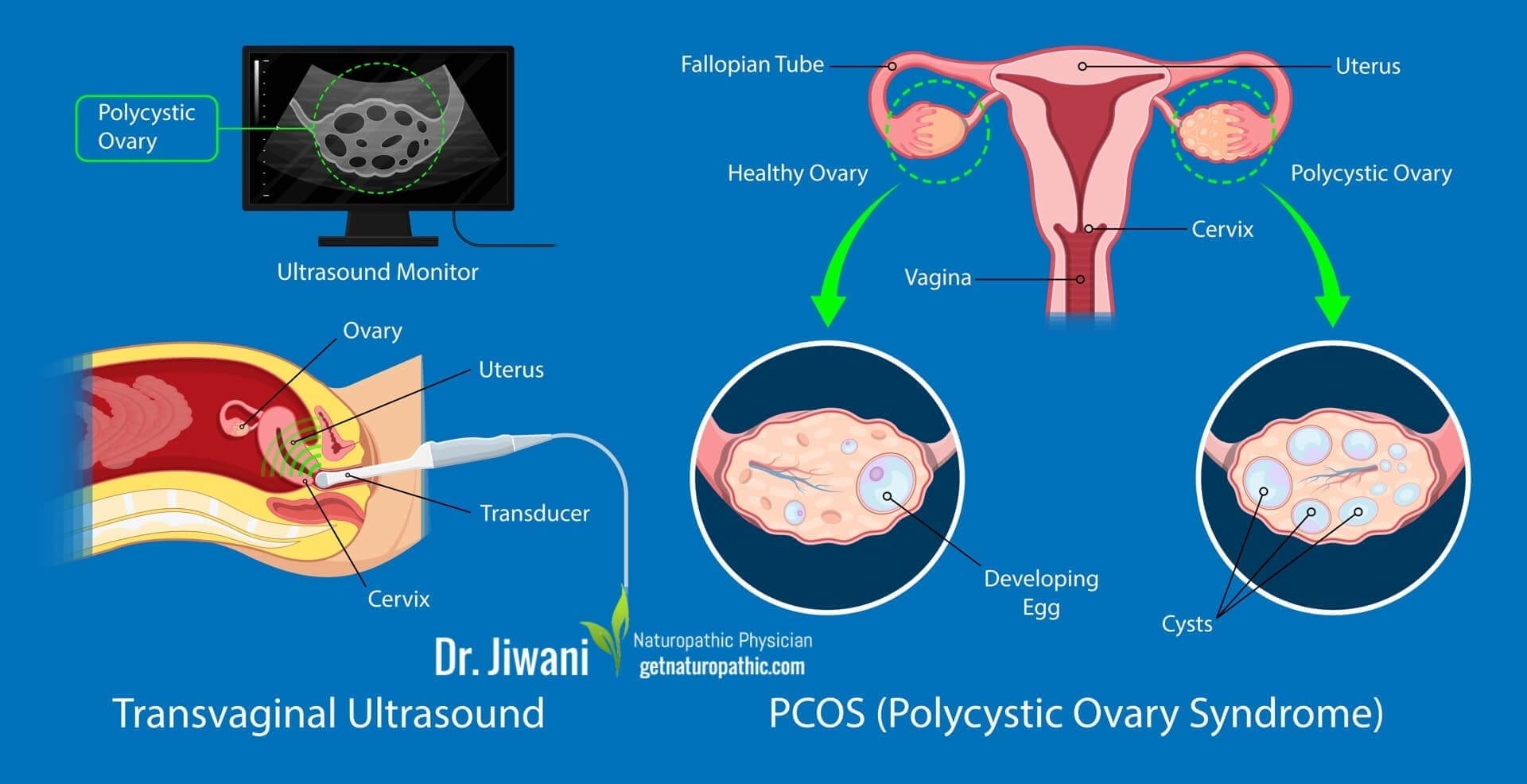
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder in fertile women suffering from obesity, high fasting insulin & insulin resistance. Since ketogenic diets improve these conditions, women with PCOS were put on a ketogenic diet. Significant improvements were seen in weight, percent free testosterone, LH/FSH ratio, and fasting insulin in women with obesity and PCOS on a ketogenic diet over 6 months (Mavropoulos, Yancy, Hepburn, & Westman, 2005).
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussions
An animal study found that the ketogenic diet after traumatic brain injury reduced lesion size by 58%. The ketogenic neuroprotection was found to be age-dependant, with younger brains having greater benefit (Prins, Fujima, & Hovda, 2005).
The ketogenic diet provides neuroprotection to both neurodegenerative diseases and traumatic brain injury & concussions through (Gasior, Rogawski, & Hartman, 2006):
- interfering with glutamate-mediated toxicity, which damages neurons
- ketones that provide the brain energy for healing and improve neuron resilience
- enhancing GABA levels
- enhancing antioxidant mechanisms to reduce oxidative damage
- protection against neuron cell death as see in seizures & ischemia, which starves the tissues of oxygen from restricted blood flow
- increasing calbindin, which buffers calcium in the cell, preventing cell death
- carbohydrate restriction which reduces oxidative stress, stabilizes cellular calcium and improves mitochondrial function (cell’s energy power plant)
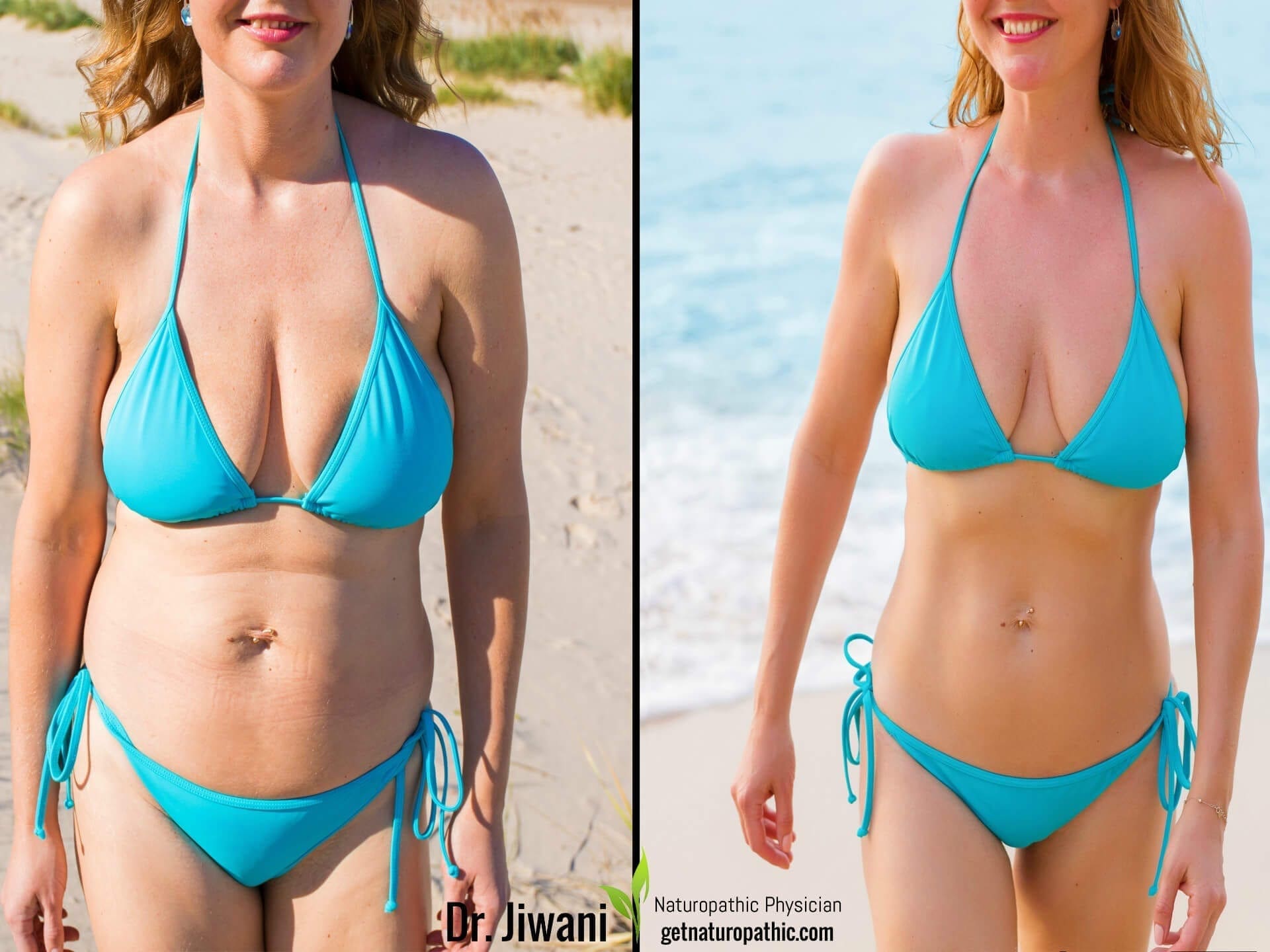
Keto Diet Health Benefits: Weight Loss
There is no doubt that ketogenic diets result in weight loss. See Keto & Weight Loss for research on the ketogenic diet & weight loss. Mechanisms to promote weight loss include appetite suppression, calorie reduction, increased fat burning, decreased fat storage, reduction in potential food allergies & resultant inflammation, increased protein intake, increased insulin sensitivity & metabolism, feeling satisfied and weight loss maintenance from hunger hormone inhibition.
Ketogenic Diet: When to Ask for Supervision
It is recommended that your should see your doctor for a health assessment before starting any dietary changes. You may want to seek the expertise of a licensed naturopathic physician to help you execute this appropriately for your health concerns.
There are some individuals that should not attempt the ketogenic diet without medical supervision by a doctor or licensed naturopathic physician.
This includes patients who are or have:
- Bariatric Surgery
- Breastfeeding
- Children
- Diabetes
- Eating Disorder
- Fever
- Gallbladder Disease or Removed
- Kidney Stones
- Mental Health Conditions
- Pancreatic Disease
- Pregnant
- Prescription Medications
- Sick with Infection
- Underweight
Related The Keto Diet for Weight Loss
Ketogenic Diet Myths
References
Freedman MR, King J, Kennedy E. Popular diets: a scientific review.
Ketogenic diet [Internet]. En.wikipedia.org. 2018 [cited 28 October 2018]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ketogenic_diet
New Adult Obesity Maps [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018 [cited 14 October 2018]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/prevalence-maps.html
Wheless JW. History of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2008 Nov;49:3-5.
Subscribe to My Blog as More Recipes & Health Nuggets will be Coming Soon…
___________________________________
This post is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan.
For further information, see Terms of Our Website.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts