Home »
Popular Posts
Coronavirus COVID-19 Clinic Closures: Dr. Jiwani, Naturopathic Physician March 20, 2020
Naturopathic Nuggets about the COVID-19 Clinic Closure
-
The clinic doors are not open for patient visits or refills per the College’s mandate and our efforts to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 virus pandemic.
- Phone consults may be scheduled as needed. This will be determined on a case-by-case basis by Dr. Jiwani.
- Refills can be done through the website PhysiciansResearch.ca or through the clinic via Canada Post shipments, although staff hours will be limited.
- Please leave a voicemail or email info@getnaturopathic.com for clarity about your specific case.
This article is dated March 20th, 2020
Coronavirus COVID-19 Clinic Closures: Dr. Jiwani, Naturopathic Physician
Dear Patients,
The COVID-19 virus pandemic represents a major public health emergency. Accordingly, I am modifying the scope of my naturopathic practice for the foreseeable future. My regulatory body, the College of Naturopathic Physicians of British Columbia (CNPBC), works to protect the public. As such, the College has strongly recommended suspending all elective and non-essential naturopathic services immediately. Additionally, in-person visits have been strongly advised against in order to prevent the spread of the Coronavirus COVID-19.
Consequently, my naturopathic clinics in both Surrey & Vancouver/Burnaby will be closed to patients for in-person visits and refills until further notice. Certain appointments that cannot be postponed may be provided by telemedicine, as determined by Dr. Jiwani, per the College regulations. We will be contacting patients this week to determine how to proceed on a case-by-case basis. All patient appointments and requests will be documented and rescheduled once in-person naturopathic services are safe to conduct. To access product refills, current patients may contact the clinic by phone or for easier access, through PhysiciansResearch.ca.
We acknowledge that these are extraordinary and stressful times. We are committed to ensuring that appropriate measures are taken to protect the community at large and our staff, while helping patients in the best way possible.
If you have questions regarding your treatment or appointments, please email us at info@getnaturopathic.com or leave a voicemail at 604.679.9988. Due to clinic closures and limited staff hours please leave a message repeating your phone number twice. We will do our best to get back to you in a timely manner. We will continue to monitor the situation daily and provide details regarding COVID-19 on our website and social media platforms, Google, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Pinterest and Linked In. Please subscribe to my blog and/or these social media accounts to ensure you receive the latest updates.
If you have an emergency, please call 911 or contact your local walk-in clinic. If you have symptoms of COVID-2019, please dial 811.
Thank you for your support, understanding and patience during this difficult time, as we work together to ensure the well-being of everyone in our community. Read the link for more information about Coronavirus: Symptoms, Prevention & Treatment of Novel Coronavirus COVID-2019.
Stay Healthy & Safe,
Dr. Jiwani & Staff
Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV (COVID-19): Resources
The information about the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) is continually being reassessed. See the resources to keep you abreast of the current status of this public health threat:
-
- World Health Organization
- World Health Organization Data Source & Map
- Centers for Disease Control & Prevention
- Government of Canada 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Latest Travel Advice
- Government of Canada 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Outbreak Update
- BC Centre for Disease Control
- Government of Ontario
- Public Health Ontario
- Infection Prevention and Control Canada
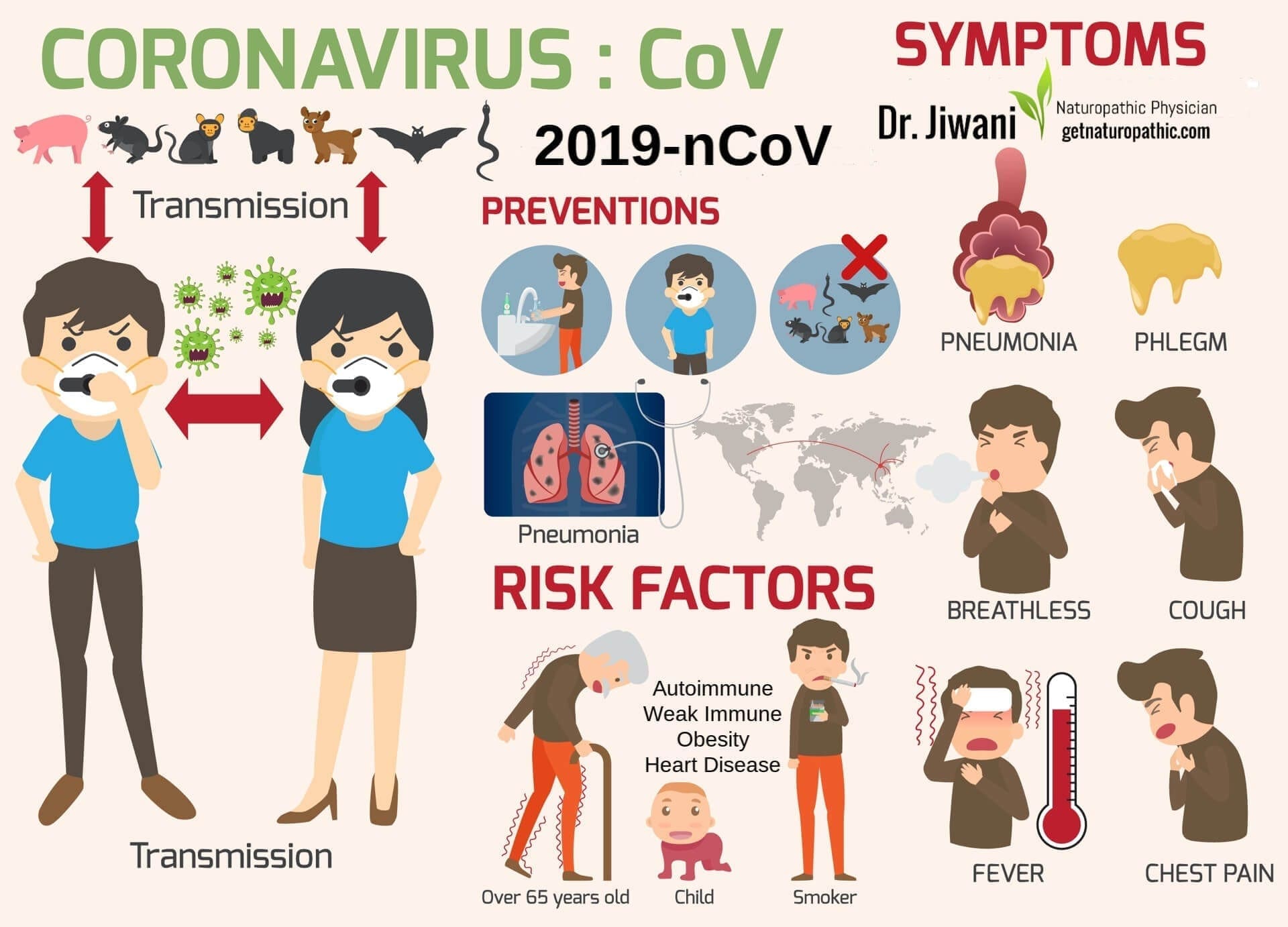
Related Coronavirus: Symptoms, Prevention & Treatment of Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV (COVID-19)
References
Advice for Public [Internet]. WHO.int. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
Backer JA, Klinkenberg D, Wallinga J. The incubation period of 2019-nCoV infections among travellers from Wuhan, China. Eurosurveillance. 2020 Jan 30 [Epub ahead of print].
Badawi A, Ryoo SG. Prevalence of comorbidities in the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2016 Aug 1;49:129-33.
Belshaw R. What is special about RNA viruses? Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2010;25(5):264-265.
Canada P. 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Outbreak Update – Canada.ca [Internet]. Canada.ca. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/2019-novel-coronavirus-infection.html
Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020 Jan 24 [Epub ahead of print].
Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Yu T. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. The Lancet. 2020 Jan 30.
Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DKW, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance. 2020 Jan 23;25:2000045.
Coronavirus (Novel) [Internet]. BCCDC.ca. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: http://www.bccdc.ca/health-professionals/clinical-resources/coronavirus-(novel)
Coronavirus [Internet]. HealthLink BC. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-feature/coronavirus
Coronavirus Infections | Coronavirus | MedlinePlus [Internet]. Medlineplus.gov. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/coronavirusinfections.html
Coronavirus [Internet]. WHO.int. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus
Guo L, Wei D, WU Y, ZHOU M, ZHANG X, Li Q, Qu J. Clinical features predicting mortality risk in patients with viral pneumonia: the MuLBSTA score. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019;10:2752.
Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, et al. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jan 31 [Epub ahead of print].
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet. 2020 Jan 24.
Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jan 29 [Epub ahead of print].
Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29 [Epub ahead of print].
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) [Internet]. En.wikipedia.org. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_East_respiratory_syndrome
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) [Internet]. World Health Organization. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/
Novel Coronavirus 2019, Wuhan, China | CDC [Internet]. CDC.gov. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/index.html
Phan LT, Nguyen TV, Luong QC, Nguyen TV, Nguyen HT, Le HQ, et al. Importation and human-to-human transmission of a novel coronavirus in Vietnam. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jan 28 [Epub ahead of print].
Q&A on Coronaviruses [Internet]. WHO.int. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
Read JM, Bridgen JRE, Cummings DAT, Ho A, Jewell CP. Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic predictions. medRxiv. 2020 Jan 28 [Epub ahead of print].
Rothe C, Schunk M, Sothmann P, Bretzel G, Froeschl G, Wallrauch C et al. Transmission of 2019-nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;.
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) [Internet]. En.wikipedia.org. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Severe_acute_respiratory_syndrome
Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Research. 2020;.
Wang W, Tang J, Wei F. Updated understanding of the outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Wuhan, China. Journal of Medical Virology. 2020 Jan 29 [Epub ahead of print].
WHO | Summary of Probable SARS Cases with Onset of Illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003 [Internet]. WHO.int. 2020 [cited 5 February 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table2004_04_21/en/
Wu JT, Leung K, Leung GM. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet. 2020 Jan 31 [Epub ahead of print].
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020 Jan 24 [Epub ahead of print].
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts