Home »
Popular Posts
Your Gluten-Free Diet is Making You Fat, Sick & Tired: the Delights & Dangers of Gluten-Free
Naturopathic Nuggets about Gluten-Free
-
North American sales of gluten-free products have risen to over 8 billion dollars as consumers believe that gluten-free products are healthier than those with gluten, paying a premium of over 200%.
-
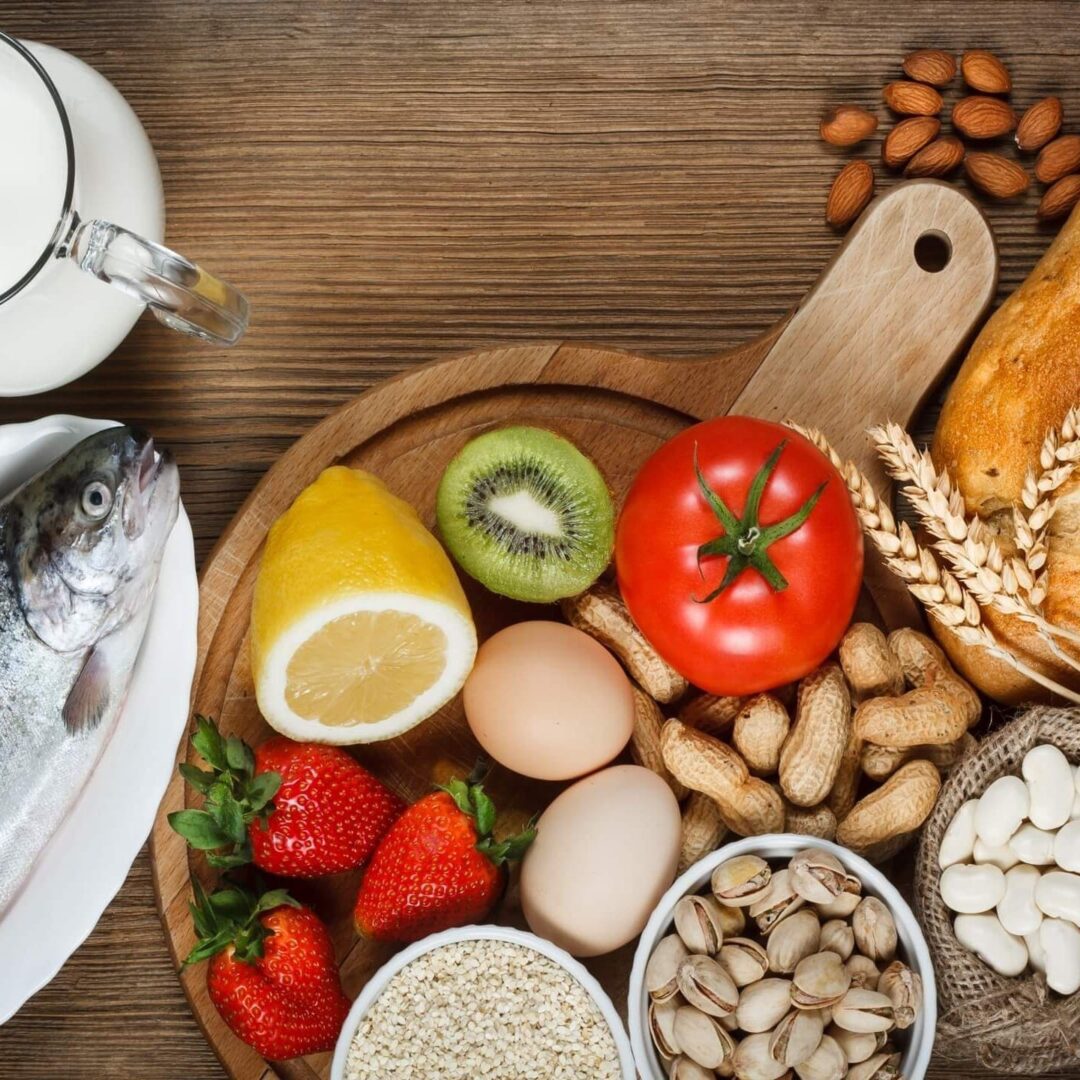
Gluten avoidance is critical in conditions such as Celiac Disease, Food Allergies to gluten & their grains, gluten sensitivity and wheat allergy.
-
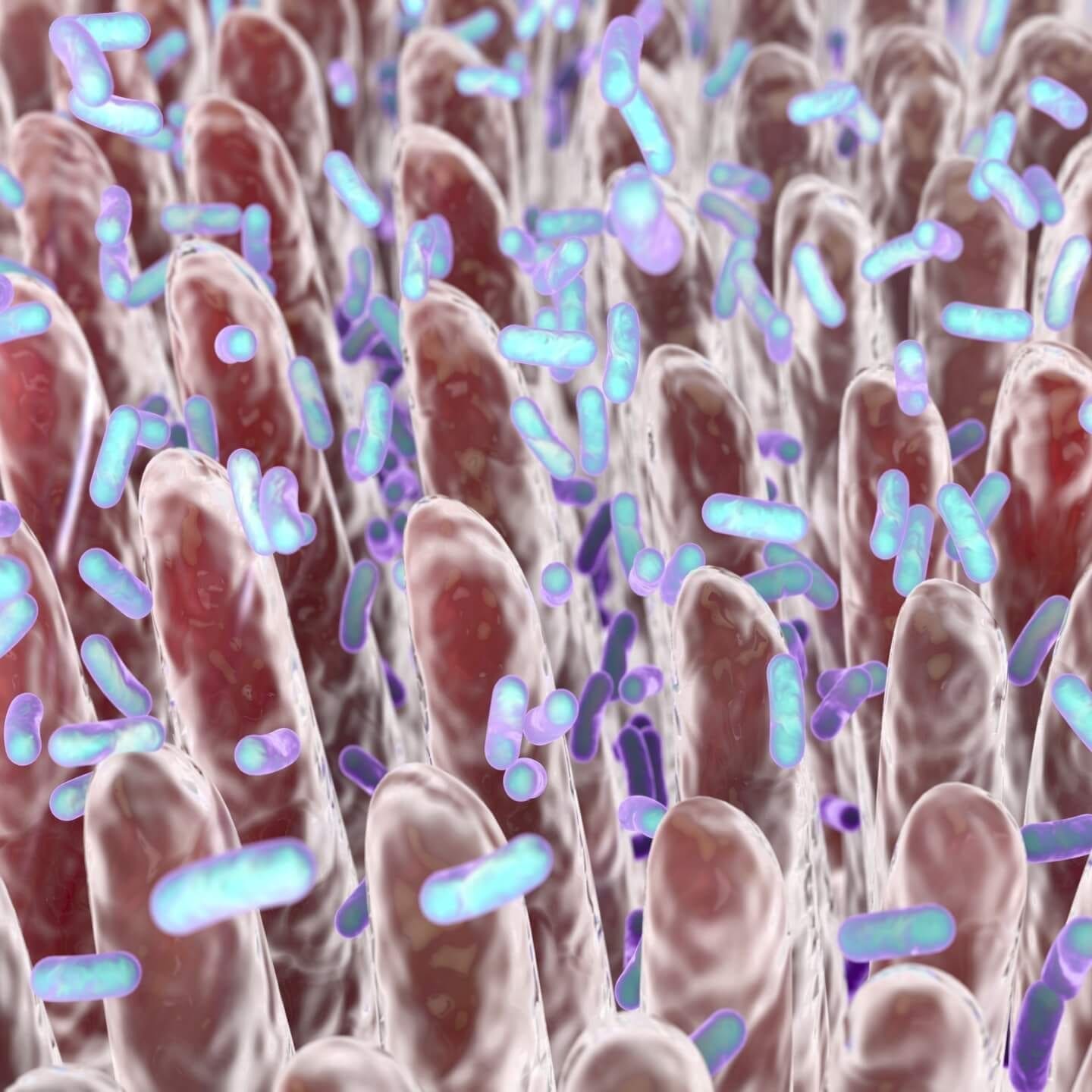
Studies have shown that consuming gluten causes a systemic immune reaction and the development of Leaky Gut Syndrome even in those without Celiac Disease.
-
Consider a Gluten-Free diet if you suffer from Autism, Cravings, Digestion issues, Poor Energy, Epilepsy, Chronic Inflammation, Food Allergies, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Malabsorption, Nutrient Deficiencies, Schizophrenia & Thyroid (Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis)
-
Gluten-Free foods that will make you fat include cookies, breads, bagels, cakes, granola, and processed dinners like macaroni & cheese. The carb counts in these foods are ridiculously high.
-
Ultimately, your body cannot tell whether its glucose (sugar) comes from bread, rice, pasta or fruit, gluten or none. Nutrients aside, a carb is a carb, and breaks down into glucose for energy. This is why a gluten-free diet can make you fat. It’s the cause & effect of consuming too many carbohydrates in any form.
The popularity of a Gluten-Free diet has escalated in the past two decades. In fact, North American sales of gluten-free products have risen to over 8 billion dollars. Consumers believe that gluten-free products are healthier than those with gluten. Meanwhile, food companies continue to market gluten-free foods as healthier and charge premium prices of over 200% for their products. Even celebrities have enhanced public awareness of gluten, espousing health benefits including weight loss. In actual fact, your gluten-free diet is likely making you fatter.
Gluten-Free Diet: Death by Gluten
Gluten avoidance is critical in conditions such as Celiac Disease, Food Allergies to gluten & their grains, gluten sensitivity and wheat allergy. Gluten is the sticky protein in grains such as wheat, barley, oat, rye, kamut, millet, spelt & triticale. The gut inflammation from gluten causes Leaky Gut Syndrome and malabsorption of nutrients including proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins & minerals. Over time, these nutrient deficiencies lead to malnutrition & generalized symptoms. It is essential to diagnose gluten-avoidance conditions such as Celiac Disease and Food Allergies to prevent life threatening issues such as Autoimmune Disorders, Neurological Deficits, Anemia, Osteoporosis & Cancer (Briani et al. 2008).
Gluten Causes Leaky Gut & Nutrient Deficiencies
Gluten-Free Diet: Autoimmune, Allergy or Sensitivity?
Many people are following Gluten-Free diets considering that Celiac Disease affects 1% of the population, while 83% are undiagnosed due to their common, vague & systemic symptoms. Gluten Sensitivities affect 5 – 10% of us (Fasano et al. 2003)(Sapone et al. 2011), and are even more common than Celiac Disease. Not to mention the many diagnosed with Gluten Allergies. Studies have shown that consuming gluten causes a systemic immune reaction and the development of Leaky Gut Syndrome even in those without Celiac Disease (Uhde et al. 2016).
Gluten can Cause Serious Damage
When to Consider a Gluten-Free Diet:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): decreased communication & social interaction (Pennesi & Klein 2012) (Ghalichi et al. 2016)
Cravings: you crave what you react to, as the foods provide a euphoric high that you constantly crave
Digestion: bloating, gas, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting (Biesiekierski et al. 2011)
Energy: fatigue, sleepy, brain fog, malabsorption & nutrient deficiencies (iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc)
Epilepsy
Food Allergies: gluten causes leaky gut, which causes you to develop food allergies
Inflammation: gluten causes chronic inflammation in the body & at the gut level (leaky gut) causing disease, fatigue, increased stress, water retention & fat gain
Insulin Resistance (Diabetes): excess glucose in the blood from repeatedly eating high carb gluten foods creates insulin resistance and eventually diabetes type 2
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): constipation, diarrhea, gas & bloating (Vazquez-Roque et al. 2013) from gluten & FODMAPS
Leaky Gut: gluten contains zonulin, a protein which damages gut lining, increasing leaky gut (intestinal permeability), allowing undigested food to enter bloodstream, causing immune reactions (developed food allergies)
Leptin Resistance: lectins in gluten affect your “full” hormone, so you are constantly hungry leading to overeating & weight gain (Jönsson et al. 2005)
Malabsorption: gluten causes leaky gut in those reactive, which leads to poor absorption of nutrients and consequent nutrient deficiencies (iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc)
Nutrient Deficiencies: gluten causes leaky gut in those reactive, which leads to poor absorption of nutrients and consequent nutrient deficiencies (iron, folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc)
Schizophrenia: (Jackson et al. 2012)(Jackson et al. 2012)
Thyroid (Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis): patients with autoimmune thyroid are 12X more likely to have gluten issues, whether from celiac disease or gluten allergy (Collin et al. 1994). Conversely, patients intolerant to gluten or celiac should have their thyroid assessed.
Gluten-Free Diet: Why is Celiac Disease So Common?
The prevalence of Celiac Disease may have escalated due to genetically modified (GMO) forms and the omnipresence of wheat in processed foods, supplements & beauty products.
Gluten Issues: It’s a Sign of the Times
Gluten-Free Diet: How to Avoid Gluten
Gluten is in foods containing wheat, barley, oat, rye, spelt, kamut, millet & triticale, durum, semolina, farro, farina, graham, wheat starch, breads, desserts, cakes, pies, pasta, cereals, french fries, processed meats, soups, sauces, brown rice syrup, soy sauce, candies, candy bars, alcohol (beer), veggie burgers, vegetarian sausage, imitation bacon, imitation seafood and malt derivatives (brewer’s yeast, malt vinegar, malt flavouring, malt syrup, beer, malted milk shakes. Products that may contain gluten include play dough, communion wafers, prescription medications, supplements, lipstick, lip gloss and balms for chapped lips (Celiac Disease Foundation).
Gluten is Everywhere so Read Labels
Gluten-Free Diet: The Carbohydrate Conundrum
Carbohydrates are sugar molecules bound together, which breaks down into glucose in the gut. Glucose is used for energy by your cells. Any excess glucose is stored as fat, clogging the arteries as cholesterol, while increasing the visceral fat around your organs, such as fatty liver. Too much sugar in the blood over time makes the insulin hormone ignore it, like a nagging husband that you learn to ignore! Essentially this is how diabetes or insulin resistance occurs. When the insulin hormone ignores the high blood sugar, it no longer goes into the cell to make energy, and stays in the blood. This makes you fat, tired & heart sick.
Excess Carbs Lead to Diabetes
Gluten-Free Diet: The Carbohydrate Addiction
Carbohydrates are found in fruits, vegetables, grains & legumes. Gluten-Free foods that will make you fat include cookies, breads, bagels, cakes, granola, and processed dinners like macaroni & cheese. The carb counts in these foods are ridiculously high. Processed grains, even gluten-free ones, spike your blood sugar, are high in calories, low in nutrients, tend to be addictive and create a roller coaster of blood sugar. You spike and then you crash.
Packaged Gluten-Free Products Make You Fat
Gluten-Free Diet: Carbs Make You Fat
Ultimately, your body cannot tell whether its glucose (sugar) comes from fruit, bread, rice or pasta, gluten or none. Nutrients aside, a carb is a carb, and breaks down into glucose for energy or is stored as fat. This is why a gluten-free diet can make you fat. It’s the cause & effect of consuming too many carbohydrates in any form. Health wise, it is ideal to get the few carbohydrates you do eat from nutrient dense sources such as fruits & vegetables.
Any & All Carbs in Excess Can Make You Fat
How to Eat Gluten-Free for Weight Loss
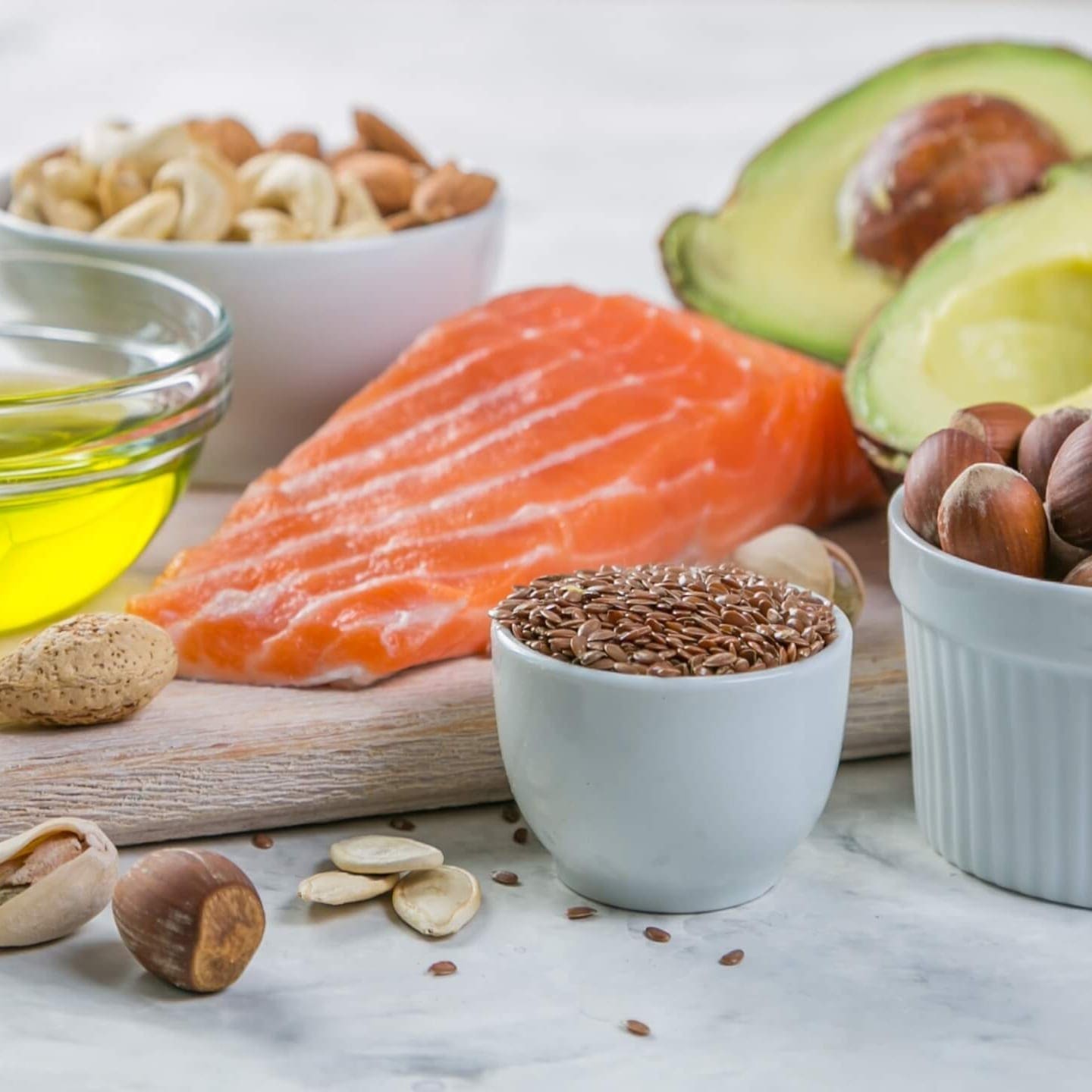
A Gluten-Free diet can help you lose weight if done mindfully. Focus on naturally occurring gluten-free foods such as organic or free range meats, organic fruits & vegetables, organic nuts & healthy fats (coconut, avocado, nut & seed butters) and fibres (flax seed, chia seed, psyllium husk). Avoid gluten-free starches including corn, potatoes, rice, tapioca starch and starchy vegetables. Use dried herbs instead of sauces which may have hidden carbs. Also, make sure to take a multivitamin-mineral for optimal nutrient status. For healthy treats that will support your weight loss goals, see Dr. Jiwani’s Naturopathic Recipes: Paleo, Keto, Vegan, Low Carb, Dairy-Free, Gluten-Free, Egg-Free, Corn-Free, Soy-Free, Sugar-Free. Please see a licensed Naturopathic Physician before starting any major health regimes for expert guidance.
Meat, Veg, Fruit & Nuts is the Recipe for Success
Related Do You Have Celiac Disease? Signs & Symptoms Of This Autoimmune Gluten Epidemic
References
Biesiekierski JR, Newnham ED, Irving PM, Barrett JS, Haines M, Doecke JD, Shepherd SJ, Muir JG, Gibson PR. Gluten causes gastrointestinal symptoms in subjects without celiac disease: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2011 Mar;106(3):508.
Briani C, Samaroo D, Alaedini A. Celiac disease: from gluten to autoimmunity. Autoimmunity Rreviews. 2008 Sep 1;7(8):644-50.
Collin P, Salmi J, Hällström O, Reunala T, Pasternack A. Autoimmune thyroid disorders and coeliac disease. European Journal of Endocrinology. 1994 Feb 1;130(2):137-40.
Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, Not T, Colletti RB, Drago S, Elitsur Y, Green PH, Guandalini S, Hill ID, Pietzak M. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2003 Feb 10;163(3):286-92.
Gaesser GA, Angadi SS. Gluten-free diet: imprudent dietary advice for the general population?. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2012 Sep 1;112(9):1330-3.
Ghalichi F, Ghaemmaghami J, Malek A, Ostadrahimi A. Effect of gluten free diet on gastrointestinal and behavioral indices for children with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized clinical trial. World Journal of Pediatrics. 2016 Nov 1;12(4):436-42.
Jackson J, Eaton W, Cascella N, Fasano A, Warfel D, Feldman S, Richardson C, Vyas G, Linthicum J, Santora D, Warren KR. A gluten-free diet in people with schizophrenia and anti-tissue transglutaminase or anti-gliadin antibodies. Schizophrenia Research. 2012 Sep;140:262.
Jackson JR, Eaton WW, Cascella NG, Fasano A, Kelly DL. Neurologic and psychiatric manifestations of celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. Psychiatric Quarterly. 2012 Mar 1;83(1):91-102.
Pennesi CM, Klein LC. Effectiveness of the gluten-free, casein-free diet for children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: based on parental report. Nutritional Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 1;15(2):85-91.
Sapone A, Lammers KM, Casolaro V, Cammarota M, Giuliano MT, De Rosa M, Stefanile R, Mazzarella G, Tolone C, Russo MI, Esposito P. Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Medicine. 2011 Dec;9(1):23.
Sources of Gluten – Celiac Disease Foundation [Internet]. Celiac Disease Foundation. 2018 [cited 26 February 2018]. Available from: https://celiac.org/live-gluten-free/glutenfreediet/sources-of-gluten/
Uhde M, Ajamian M, Caio G, De Giorgio R, Indart A, Green PH, Verna EC, Volta U, Alaedini A. Intestinal cell damage and systemic immune activation in individuals reporting sensitivity to wheat in the absence of coeliac disease. Gut. 2016 Jul 21:gutjnl-2016.
Vazquez–Roque MI, Camilleri M, Smyrk T, Murray JA, Marietta E, O’Neill J, Carlson P, Lamsam J, Janzow D, Eckert D, Burton D. A controlled trial of gluten-free diet in patients with irritable bowel syndrome-diarrhea: effects on bowel frequency and intestinal function. Gastroenterology. 2013 May 1;144(5):903-11.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts