Home »
Popular Posts
Autoimmune Disease: Signs, Symptoms, Conditions & Treatments
Naturopathic Nuggets about Autoimmune Disease
- Over 50 million North Americans suffer from Autoimmune Diseases, of which almost 75% are women. It can happen to anyone, if it’s in their genes
- With Autoimmune Diseases, the immune system goes haywire, confusing the tissues of the body as foreign, and attacks them
- Mental, emotional & physical stressors trigger Autoimmune Disease, of which food allergies are the biggest physical stressor causing Autoimmunity.
- Autoimmune Diseases cause inflammation which destroys the body’s tissues, affecting function
- Symptoms of Autoimmune Disease can be vague, delayed & systemic, including anxiety, fatigue, digestive disturbances, hair loss, headaches, rashes, recurrent infections, joint or muscle pain, weight gain or loss
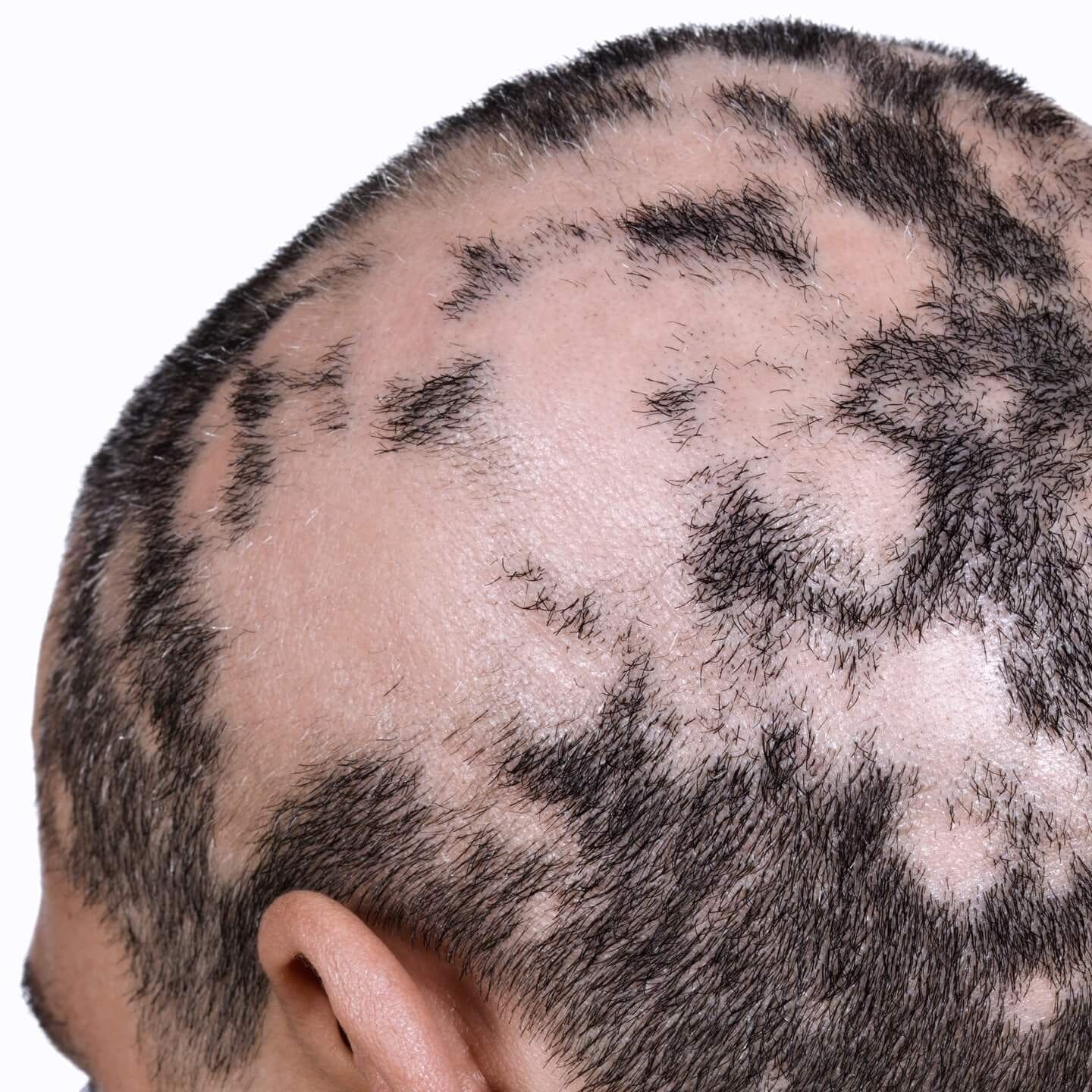
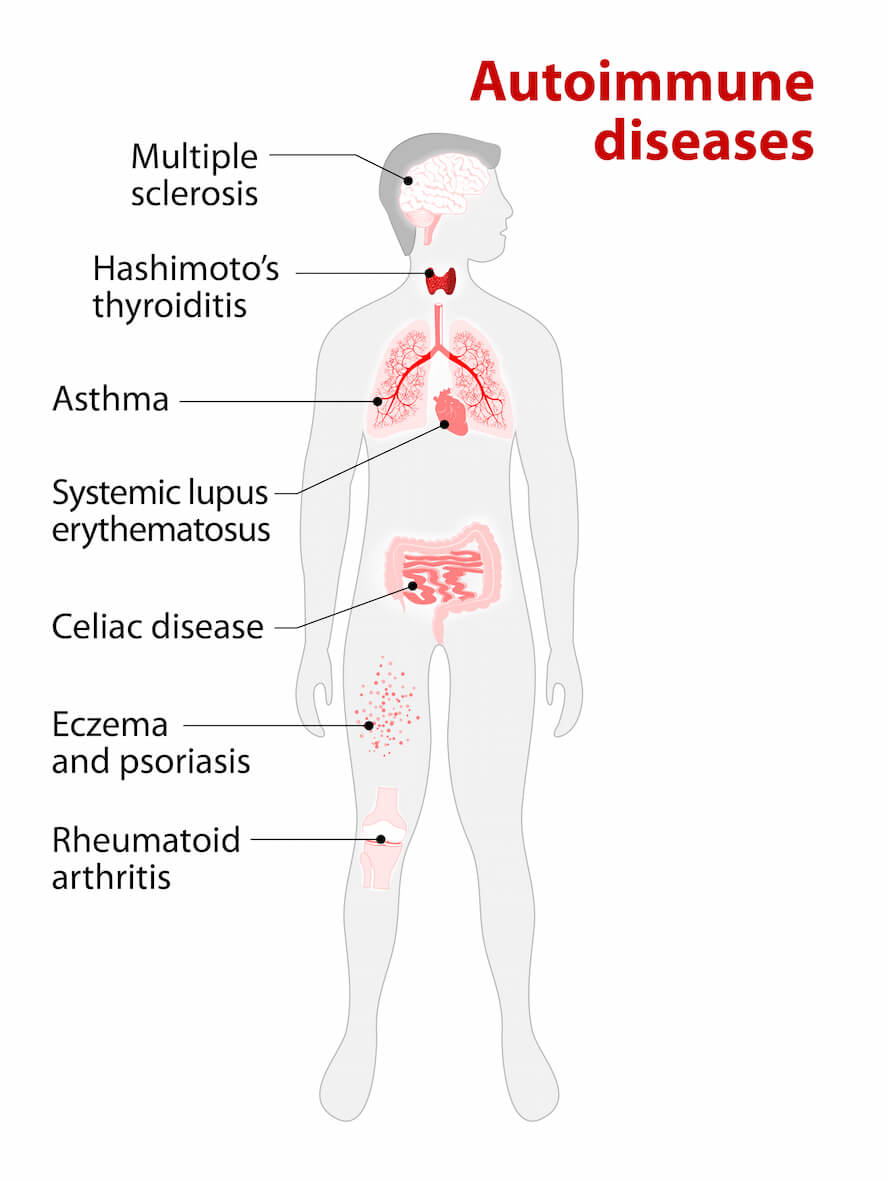
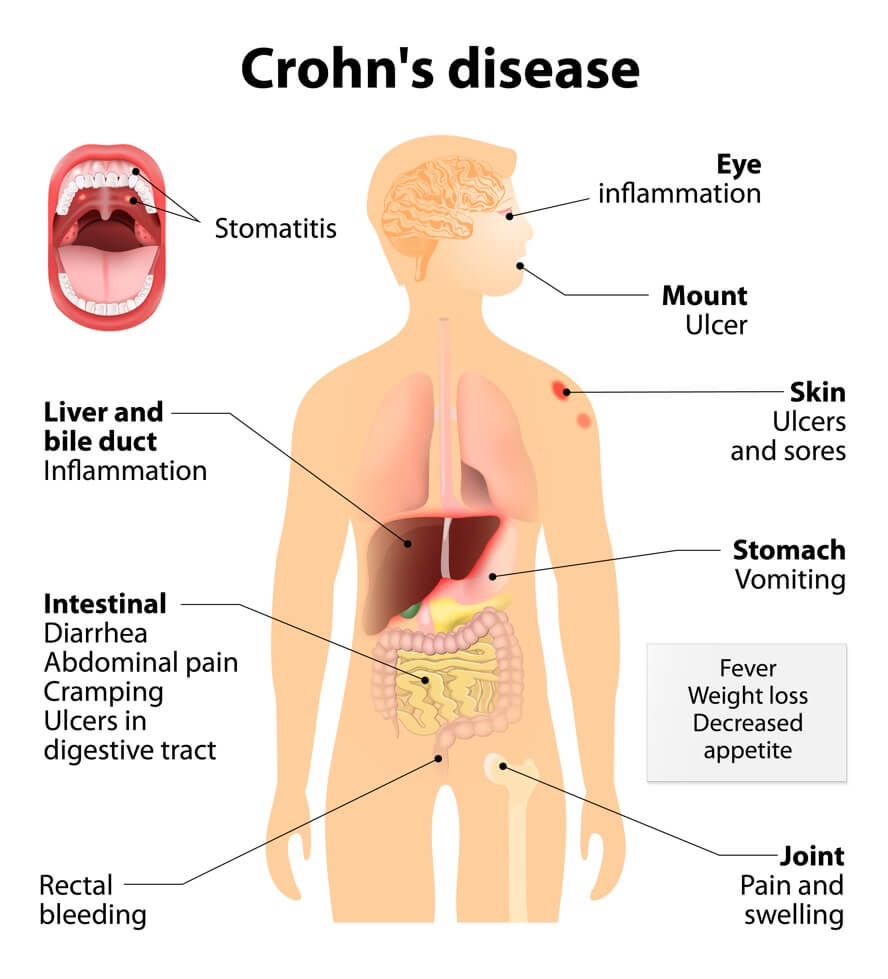
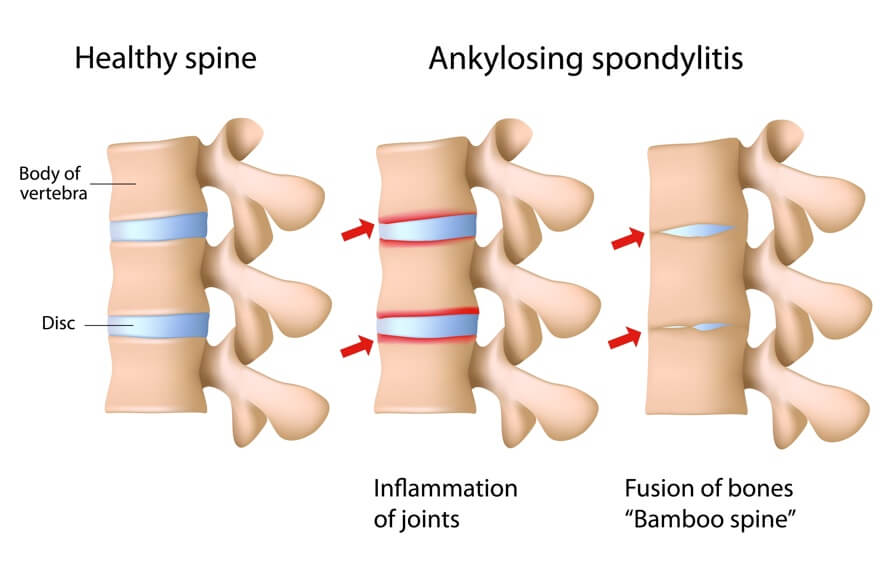
- Common Autoimmune Diseases include Alopecia (hair loss), Ankylosing Spondylitis (spine), Celiac Disease, Hashimoto’s / Graves Disease (thyroid), Lupus / SLE (whole body), Multiple Sclerosis (nerves), Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis (skin & joints), Rheumatoid Arthritis (joints), Ulcerative Colitis / Crohn’s Disease (bowels), Vitiligo (skin)
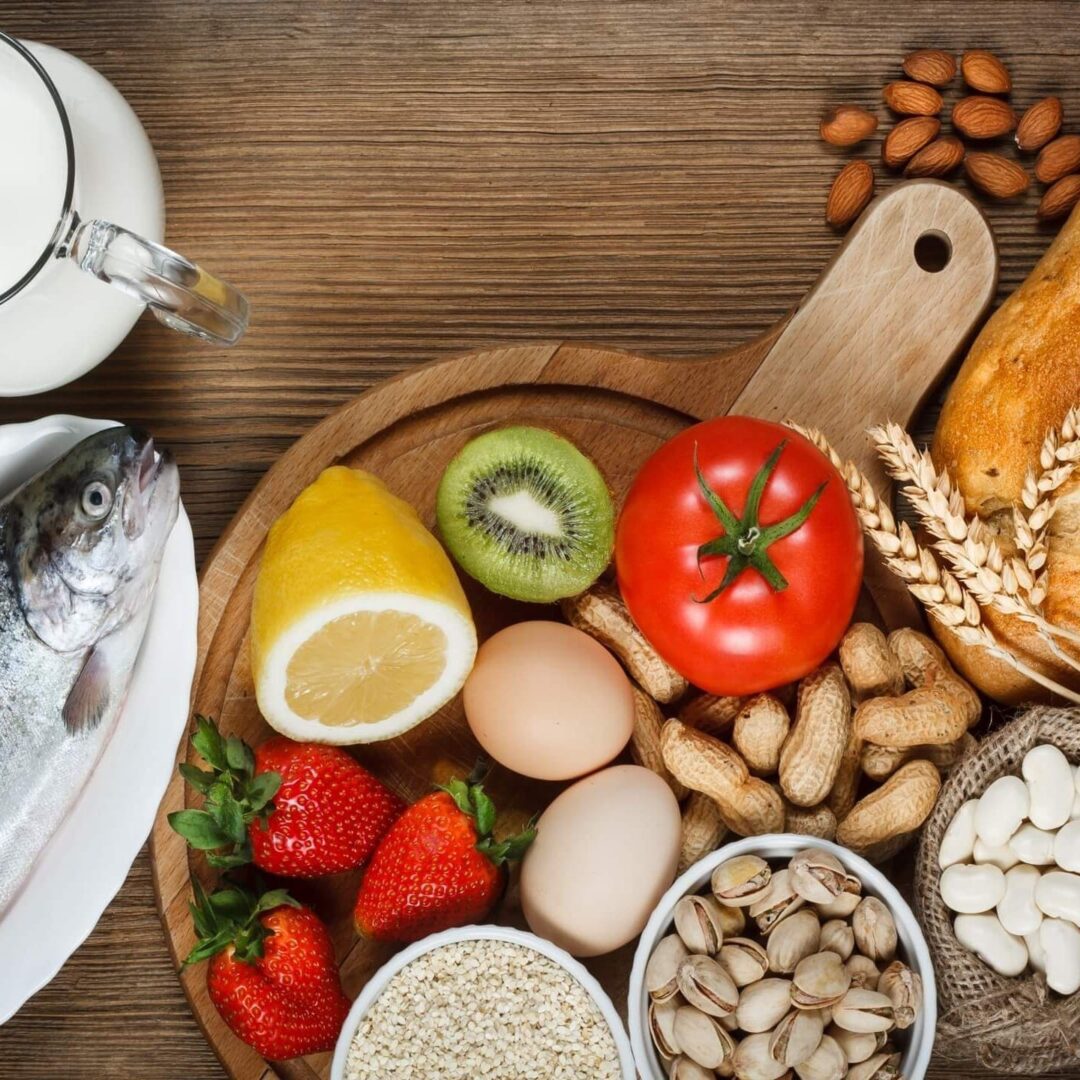
- Food Allergies cause inflammation that triggers Autoimmunity, Dysbiosis & Leaky Gut Syndrome
- Microbiome war within the gut determines health, as declining levels of “good” bacteria allow overgrowth of harmful bacteria, yeast & parasites to damage gut health and thus health overall. This is called Dysbiosis which leads to Leaky Gut Syndrome, commonly implicated in Autoimmune Diseases.
- It is advisable to seek professional advice from a licensed Naturopathic Physician, after consulting a Medical Doctor, due to the seriousness & aggressiveness of Autoimmune Diseases
The Autoimmune Epidemic
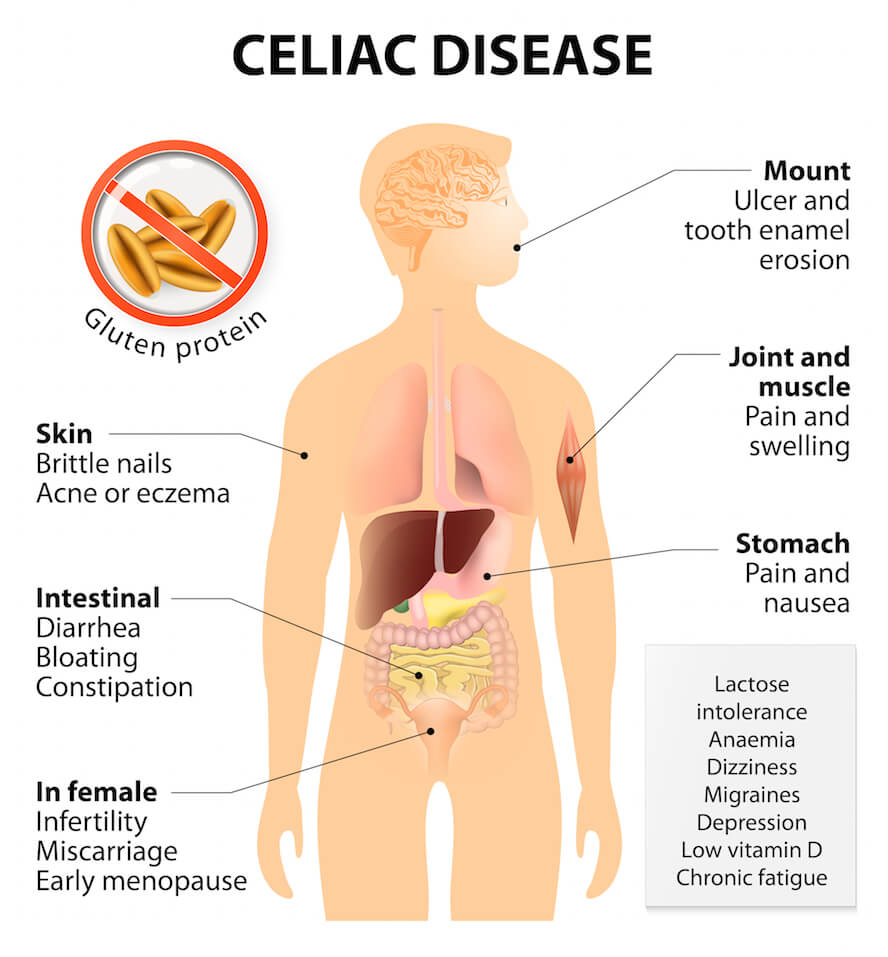
Over 50 million North Americans suffer from Autoimmune Diseases, and almost 75% are women. An Autoimmune Disease is an abnormal response to normal immune function. The incidence of Celiac Disease is skyrocketing. Of the three million North Americans suffering from the symptoms of Celiac Disease, approximately 83% are undiagnosed, as the symptoms are diverse, common & systemic.
Autoimmunity Prevails in a Weakened, Stressed & Toxic Society
Immunity can be Healthy or Haywire
Normally, the immune system attacks foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and cancer cells that can harm the body. A healthy immune system innately knows not to attack the body’s own tissues. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system goes haywire, confusing the tissues of the body as foreign, and attacks them.
Autoimmune is When the Immunity Turns Against the Body
Autoimmune: The Immune Giant is Awake & Crazy
Autoimmune Disease is like a crazy, sleeping giant, lying dormant in the genes. This giant is powerful and when the body is healthy, he protects it. In those with Autoimmune genetics, the powerful giant wakes up, goes crazy, and starts attacking the body, working against it.
The Immune Giant Can Be Healthy Or Crazy
Autoimmune Disease: Why Some and Not Others?
What triggers an autoimmune disease is not completely understood conventionally. It has been extrapolated that certain individuals that have a genetic predisposition to this abnormal immunity, can trigger this cascade of damage.
Autoimmunity: It’s In The Genes!
Autoimmune: What Wakes Up The Crazy Giant?
Autoimmune Disease means the body has been stressed enough to trigger the negative expression of one’s own genetics. These stressors may come in the form of mental, emotional and physical forms. Physical stressors may include food allergies, toxins, drugs, bacteria or viruses. These stressors can lead to Dysbiosis, causing a cascade of inflammatory damage leading to Leaky Gut Syndrome, which initiates or aggravates Autoimmune Diseases.
Food Allergies Cause Autoimmunity
Autoimmune & Inflammation: The Cause & Effect
The pathway of damage of Autoimmune Disease is inflammation, which results in the destruction of various body tissues, abnormal growth of the organ and/or changes to its function.
The symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases depend on where the inflammatory damage occurs, and in which tissues. General symptoms reflect the immune response, and may be temporary or long term.
Autoimmune Causes Inflammation, Inflammation Destroys the Tissues
Autoimmune Signs & Symptoms
Generalized Autoimmune Disease Symptoms may include:
- Anxiety
- Adrenal Fatigue “Wired but Tired”
- Attention Deficit &/ Hyperactivity
- Brain Fog
- Digestion Issues (Inflammatory Bowel Disease IBD): Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Constipation, Cramping. Diarrhea, Gas
- Fatigue, Low Energy, Exhaustion
- Fever
- Headaches
- Joint Pain & Stiffness
- Lethargy & Malaise
- Muscle Pain & Weakness
- Rashes: Acne, Dermatitis, Eczema, Psoriasis, Rosacea
- Recurrent Infections
- Weight Gain or Weight Loss
Autoimmune Symptoms Can Be Vague, Delayed & Affect the Whole Body
Autoimmune Diseases: How & Where?
There are many types of autoimmune diseases, divided into whether it affects a specific organ or whether it causes symptoms throughout the body.
Affects a Specific Organ:
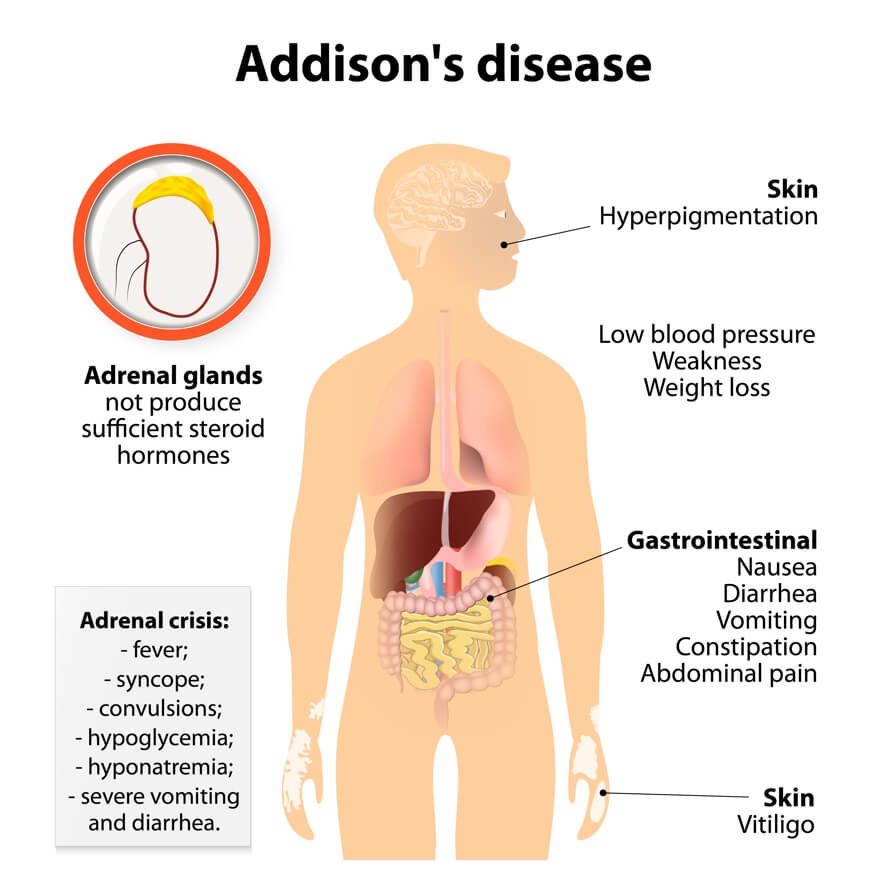
- Adrenal Glands: Addison’s Disease
- Bladder: Interstitial Cystitis
- Intestines: Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis
- Esophagus: Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- Eyes: Iritis related to Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Kidneys: IgA Nephropathy
- Liver: Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Muscles: Myasthenia Gravis
- Nervous System: Multiple Sclerosis
- Pancreas: Diabetes Type I
- Salivary Glands: Sjogren’s Syndrome
- Skin: Lichen Planus
- Skin: Vitiligo
- Spine: Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Stomach: Pernicious Anemia
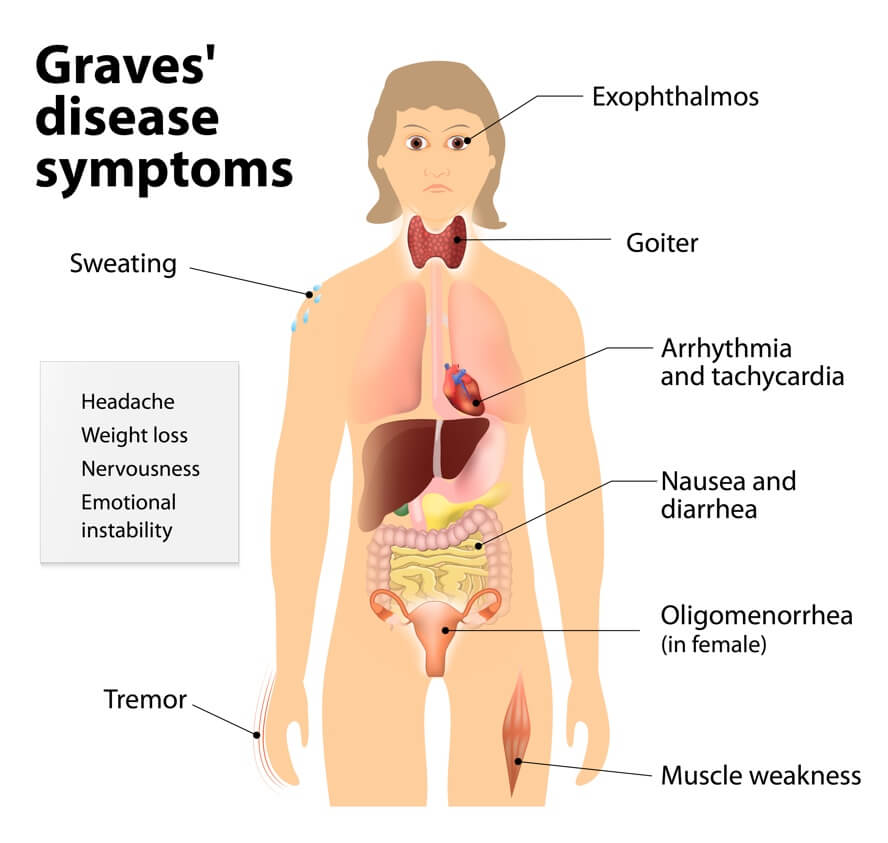
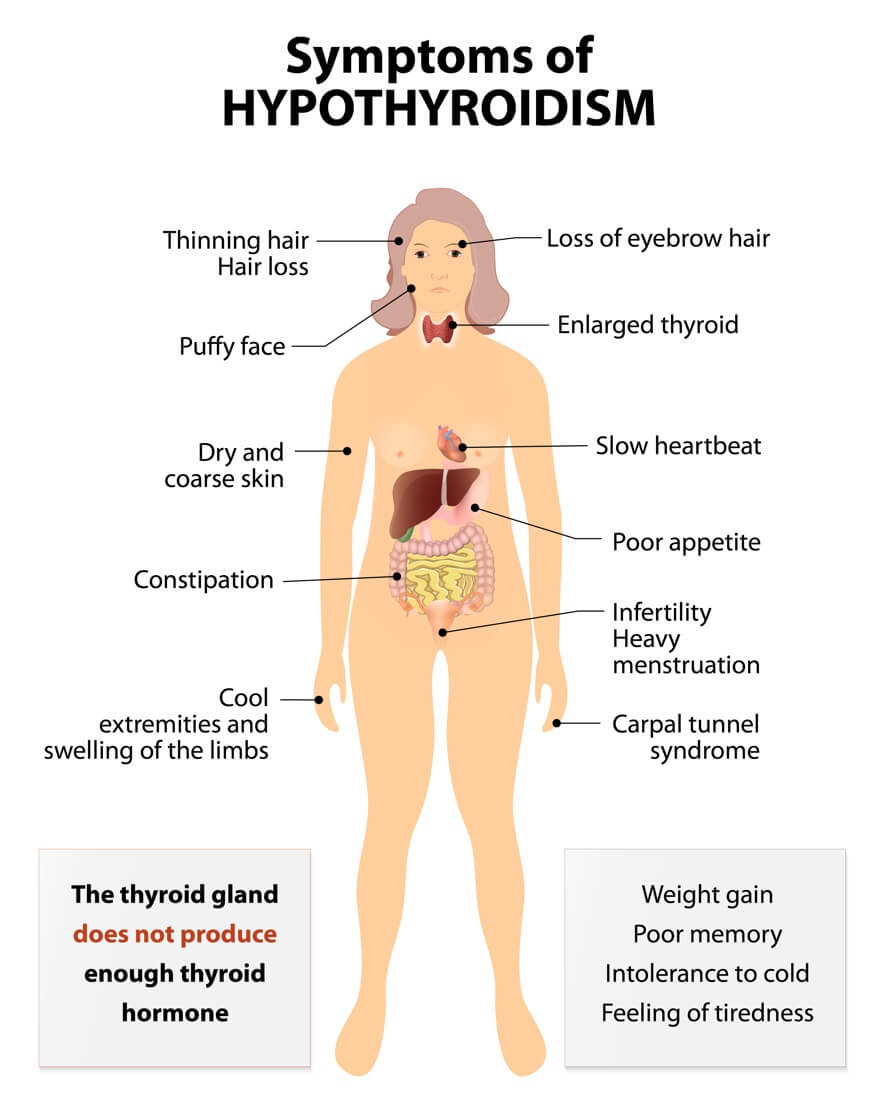
- Thyroid: Hashimoto’s / Graves Disease
Affects the Whole Body:
- Alopecia Areata: Hair Loss in Scalp, Face, Body
- Celiac Disease: Small Intestine Damage from eating Gluten, causing malabsorption, nutrient deficiencies, malnutrition, weight loss
- Dermatomyositis: Inflammation of Muscles, Skin Rash
- Lupus / SLE: Rash, Fatigue
- Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joint Pain
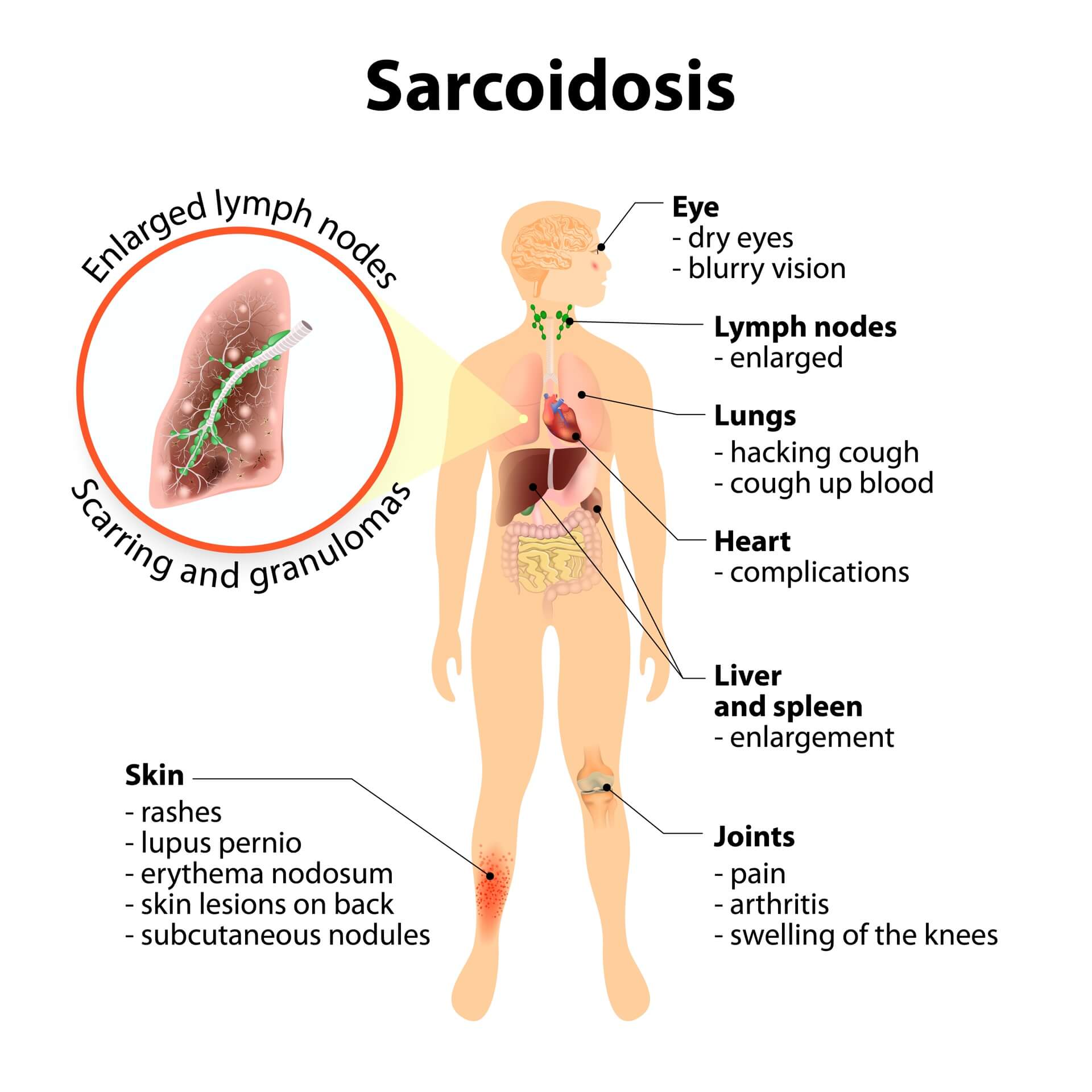
- Sarcoidosis: Lungs, Skin, Lymph nodes
- Scleroderma: Hardens Skin & Connective Tissue
Autoimmune Disease & Leaky Gut Syndrome
Naturopathic Physicians have been diagnosing Leaky Gut Syndrome for decades, in their quest for treating the cause(s) in patients suffering from Indigestion, Allergies, Hormonal Imbalance, Brain, Skin & Autoimmune Diseases. Only recently has Leaky Gut Syndrome become more mainstream as scientists are investigating the profound link between Leaky Gut and various chronic diseases including Autoimmune Diseases. Physically this is because 70% of your immunity lies in your gut’s lymph system, GALT meaning gut-associated lymphoid tissue.
Leaky Gut is Chronic Inflammation Linked to Many Health Conditions
Leaky What Now?
Much of our North American population unknowingly struggles with Leaky Gut given our society’s poor diet, toxic exposures and chronic stress. Although a century of documentation exists, Medical Doctors are finally acknowledging the validity of this affliction.
Leaky Gut is Caused by Diet, Stress & Toxicity
Autoimmune & Leaky Gut
You would think that Leaky Gut Syndrome would target digestive function only. In fact, Leaky Gut Syndrome is the cause for many severe & chronic health conditions, as bowel health determines overall health.
“All Disease Begins In The Gut” ~ Hippocrates
Autoimmune & Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis is an unhealthy bowel environment which occurs with an imbalance of bad guys versus good guys (Probiotics) in the bowel. This war within the gut determines health, as declining levels of “good” bacteria allow overgrowth of harmful bacteria (C.difficile, Salmonella, E.coli), yeast (Candidiasis) & parasites to damage the gut (Leaky Gut Syndrome) & health overall including causing Autoimmune Disease.
Dysbiosis: Losing the War Within
Certain factors cause this negative microbiome Dysbiosis, as increased yeast, bad bacteria & parasites overpower the good bacteria. The toxins produced from Dysbiosis triggers inflammation which leads to changes in intestinal permeability (Leaky Gut Syndrome) & Autoimmune Diseases in those genetically predisposed.
Dysbiosis – Leaky Gut – Autoimmune Connection
Conventional Treatments for Autoimmune Diseases
Conventional Medicine (MDs):
The goal of treatment is to:
- Suppress Symptoms
- Suppress the Immunity with Steroids such as Prednisone, Biologics
Naturopathic Medicine (Dr. Jiwani, Licensed Naturopathic Physician):
The goal of treatment is to:
- Reduce Symptoms by Treating the Causes
- Normalize & Support the Immunity
- Address Underlying Deficiencies resulting from the Autoimmune Disease Process i.e. hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies etc
- Create an Individualized Treatment Plan Specific for the Patient through addressing Food Allergies, Dysbiosis, Leaky Gut, Improving Digestion, Absorption & Nutrient Status, and Balancing Hormones, whether Stress Hormones, Sexual Hormones, Thyroid Hormones or Insulin Hormone Regulation
Treat the Causes to Resolve the Symptoms
How to Normalize Immunity and Calm the Autoimmune Giant
The key to health when you suffer from Autoimmune Disease(s) is a multi-pronged approach.
Supplement with Human Strain Probiotics:
Not all probiotics are the same, and unfortunately vegetarian & dairy forms through food & supplements are rejected within 48 hours as the body knows plant or animal (cow) sources are foreign. Human strains allow long term implantation of bacteria for long lasting effectiveness. This improves Dysbiosis. Otherwise, it is like trying to fill up a bucket with a hole in it.
Probiotics may be indicated for those with:
-
- ADHD & Autism
- Autoimmune Disease
- Allergic Sinusitis
- Candidiasis, Yeast Infections, Fungal Infections
- Celiac Disease
- Diarrhea, Constipation
- Food Allergies
- Gastrointestinal Infection (Gastroenteritis)
- Heavy Metal Toxicity
- Intestinal Dysbiosis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Lactose Intolerance
- Leaky Gut or Compromised Intestinal Permeability
- Malabsorption (Nutritional Deficiencies: Iron, B12, Vitamin D)
Eat Prebiotics:
One of the best ways to support optimal growth of your gut bacteria is to eat foods that contain prebiotics, such as garlic, onions, leeks, apples, konjac root (shirataki noodles), cacao (chocolate), flaxseeds, jicama root & seaweed.
Minimize Carbs & Sugars:
Excess carbohydrates in any form, whether from fruit, grains, starchy vegetables, juices & soda pop, feed the bad bacteria, yeast & parasites, promoting Dysbiosis. A recent study exemplifies this with a microbiome restoration diet which improves digestion, cognition, physical and emotional wellbeing (Lawrence & Hyde 2017)
Identify & Avoid Food Allergies:
Consuming food allergies promotes inflammation, Dysbiosis and causes Leaky Gut Syndrome. Inflammation at the gut level causes bacterial imbalance, poor digestion & malabsorption which promotes intestinal permeability or leaky gut. Once dysbiosis persists, opportunistic bacteria, yeast & parasites can overgrow, harming health such as causing Autoimmune Diseases, perpetuating cravings, mood changes & weight gain.
Avoid Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol is a form of yeast, which should be avoided in those allergic to yeast and/or suffering from Candidiasis (systemic yeast infection in the blood). Additionally, alcohol will trigger inflammatory & toxic pathways by altering gut bacteria balance (Dysbiosis), increasing inflammatory toxin release from bacteria, while disrupting your intestinal barrier (Leaky Gut Syndrome) allowing more inflammatory toxins into the bloodstream, worsening Autoimmune conditions.
Discourage Bad Guys:
Nutrition, immunity, lack of toxicity and overall health depends upon the health of the gastrointestinal tract. Poor gut health is called Leaky Gut Syndrome. The key to optimal gut health is to increase the amount of the “good guys” (probiotics) in the bowel and to kill the “bad guys” (Yeast, Fungus, Viruses, Bad Bacteria & Parasites) thereby promoting a healthy microbiome.
When the “bad guys” take over, they wreak havoc in the body, ravaging tissues with the harmful toxins they release. This unfavourable environment in the gut is called Intestinal Dysbiosis which leads to Leaky Gut Syndrome, and vice versa.
The formulation Yeast-X attacks the “bad guys”, prevents their growth and promotes a healthy gastrointestinal tract through good bacteria balance or a healthy microbiome. Yeast-X is indicated for those with unhealthy diets, history of chronic antibiotic use and/or recurrent infections, or overgrowth of disease-causing microbes such as Clostridium difficile, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) or Candida albicans. Yeast-X provides the potent anti-fungal effect of Undecylenic Acid for systemic yeast infections (Candidiasis), and is two thousand times (2000%) stronger than common anti-fungal agents (Caprylic Acid) and Oregano Oil.
Taking Yeast-X facilitates a successful biochemical shift from intestinal dysbiosis (a diseased environment) to eubiosis (a healthy environment), through inhibition of the pathogenic fungal, viral and bacterial culprits which can aggravate your Autoimmune Disease.
My Autoimmune Health Story…
Read about what Dr. Jiwani has been through and how her personal experience with several, serious Autoimmune Diseases can help you.
Related Food Allergies: When Friend Becomes Foe
References
Alcock J, Maley CC, Aktipis C. Is eating behavior manipulated by the gastrointestinal microbiota? Evolutionary pressures and potential mechanisms. Bioessays. 2014 Oct 1;36(10):940-9.
Anders HJ, Andersen K, Stecher B. The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney International. 2013 Jun 1;83(6):1010-6.
Arrieta MC, Bistritz L, Meddings JB. Alterations in intestinal permeability. Gut. 2006 Oct 1;55(10):1512-20.
Barau E, Dupont C. Modifications of intestinal permeability during food provocation procedures in pediatric irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology And Nutrition. 1990 Jul 1;11(1):72-7.
Benard A, Desreumeaux P, Huglo D, Hoorelbeke A, Tonnel AB, Wallaert B. Increased intestinal permeability in bronchial asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1996 Jun 30;97(6):1173-8.
Brown K, DeCoffe D, Molcan E, Gibson DL. Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients. 2012 Aug 21;4(8):1095-119.
Campbell AW. Autoimmunity and the Gut. Autoimmune Diseases. 2014 May 13;2014.
Conlon MA, Bird AR. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients. 2014 Dec 24;7(1):17-44.
de Magistris L, Familiari V, Pascotto A, Sapone A, Frolli A, Iardino P, Carteni M, De Rosa M, Francavilla R, Riegler G, Militerni R. Alterations of the intestinal barrier in patients with autism spectrum disorders and in their first-degree relatives. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology And Nutrition. 2010 Oct 1;51(4):418-24.
Fasano A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 2012 Feb 1;42(1):71-8.
Fasano A. Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2012 Jul 1;1258(1):25-33.
Hollander D. Intestinal permeability barrier in Crohn’s disease: the difficulty in shifting the paradigm. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2013 Jul 1;58(7):1827.
Hulston CJ, Churnside AA, Venables MC. Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects. British Journal of Nutrition. 2015 Feb 28;113(04):596-602.
Humbert P, Bidet A, Treffel P, Drobacheff C, Agache P. Intestinal permeability in patients with psoriasis. Journal of Dermatological Science. 1991 Jul 1;2(4):324-6.
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Hyland NP. Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2015 Oct 14;9:392.
Kiraly DD, Walker DM, Calipari ES, Labonte B, Issler O, Pena CJ, Ribeiro EA, Russo SJ, Nestler EJ. Alterations of the host microbiome affect behavioral responses to cocaine. Scientific Reports. 2016;6.
Lawrence K, Hyde J. Microbiome restoration diet improves digestion, cognition and physical and emotional wellbeing. PLOS ONE. 2017;12(6):e0179017.
Lauret E, Rodrigo L. Celiac disease and autoimmune-associated conditions. BioMed Research International. 2013 Jul 24;2013.
Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Jamar F, Stärkel P, Windey K, Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F, Verbeke K, De Timary P. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2014 Oct 21;111(42):E4485-93.
Li Q, Lauber CL, Czarnecki-Maulden G, Pan Y, Hannah SS. Effects of the Dietary Protein and Carbohydrate Ratio on Gut Microbiomes in Dogs of Different Body Conditions. mBio. 2017 Mar 8;8(1):e01703-16.
Maes M, Mihaylova I, Leunis JC. Increased serum IgA and IgM against LPS of enterobacteria in chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS): indication for the involvement of gram-negative enterobacteria in the etiology of CFS and for the presence of an increased gut–intestinal permeability. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2007 Apr 30;99(1):237-40.
Maes M, Kubera M, Leunis JC, Berk M. Increased IgA and IgM responses against gut commensals in chronic depression: further evidence for increased bacterial translocation or leaky gut. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2012 Dec 1;141(1):55-62.
Marí-Bauset S, Zazpe I, Mari-Sanchis A, Llopis-González A, Morales-Suárez-Varela M. Evidence of the gluten-free and casein-free diet in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Journal of Child Neurology. 2014 Dec;29(12):1718-27.
Michielan A, D’Incà R. Intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis, clinical evaluation, and therapy of leaky gut. Mediators of Inflammation. 2015 Oct 25;2015.
Montiel-Castro AJ, González-Cervantes RM, Bravo-Ruiseco G, Pacheco-López G. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: neurobehavioral correlates, health and sociality. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience. 2013;7.
Myers SP. The causes of intestinal dysbiosis: a review. Alternative Medicine Review. 2004 Jun;9(2):180-97.
Patil AD. Link between hypothyroidism and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Indian Journal Of Endocrinology And Metabolism. 2014 May;18(3):307.
Pedersen L, Parlar S, Kvist K, Whiteley P, Shattock P. Data mining the ScanBrit study of a gluten-and casein-free dietary intervention for children with autism spectrum disorders: behavioural and psychometric measures of dietary response. Nutritional Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 1;17(5):207-13.
Pennesi CM, Klein LC. Effectiveness of the gluten-free, casein-free diet for children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: based on parental report. Nutritional Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 1;15(2):85-91.
Perrier C, Corthesy B. Gut permeability and food allergies. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2011 Jan 1;41(1):20-8.
Rapin JR, Wiernsperger N. Possible links between intestinal permeablity and food processing: a potential therapeutic niche for glutamine. Clinics. 2010;65(6):635-43.
Rosenfeldt V, Benfeldt E, Valerius NH, Pærregaard A, Michaelsen KF. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and small intestinal permeability in children with atopic dermatitis. The Journal of Pediatrics. 2004 Nov 30;145(5):612-6.
Santocchi E, Guiducci L, Fulceri F, Billeci L, Buzzigoli E, Apicella F, Calderoni S, Grossi E, Morales MA, Muratori F. Gut to brain interaction in Autism Spectrum Disorders: a randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 4;16(1):183.
Smith MD, Gibson RA, Brooks PM. Abnormal bowel permeability in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 1985;12(2):299-305.
Vaarala O. Leaking gut in type 1 diabetes. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 2008 Nov 1;24(6):701-6.
Whiteley P, Shattock P, Knivsberg AM, Seim A, Reichelt KL, Todd L, Carr K, Hooper M. Gluten-and casein-free dietary intervention for autism spectrum conditions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2012;6.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts