Home »
Popular Posts
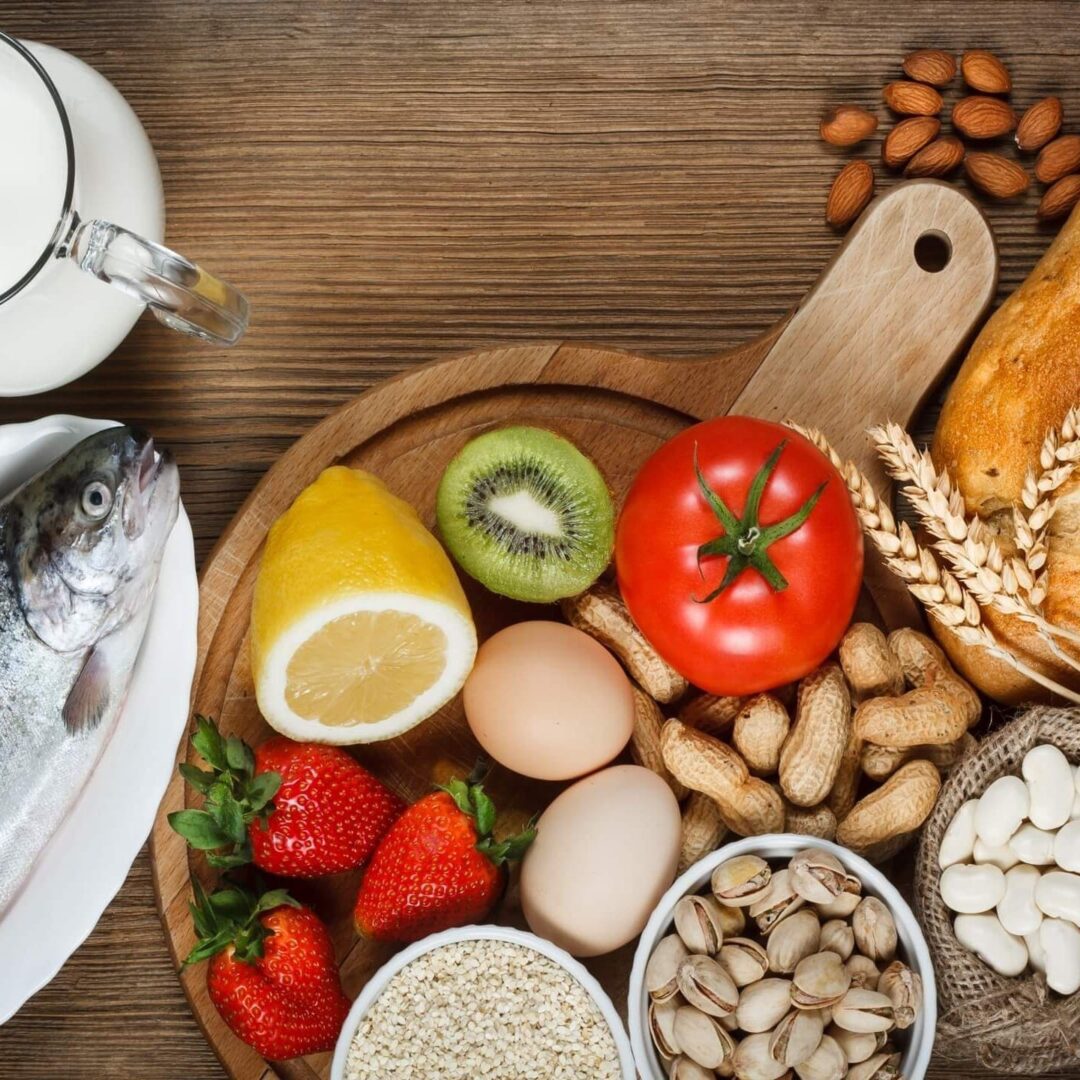
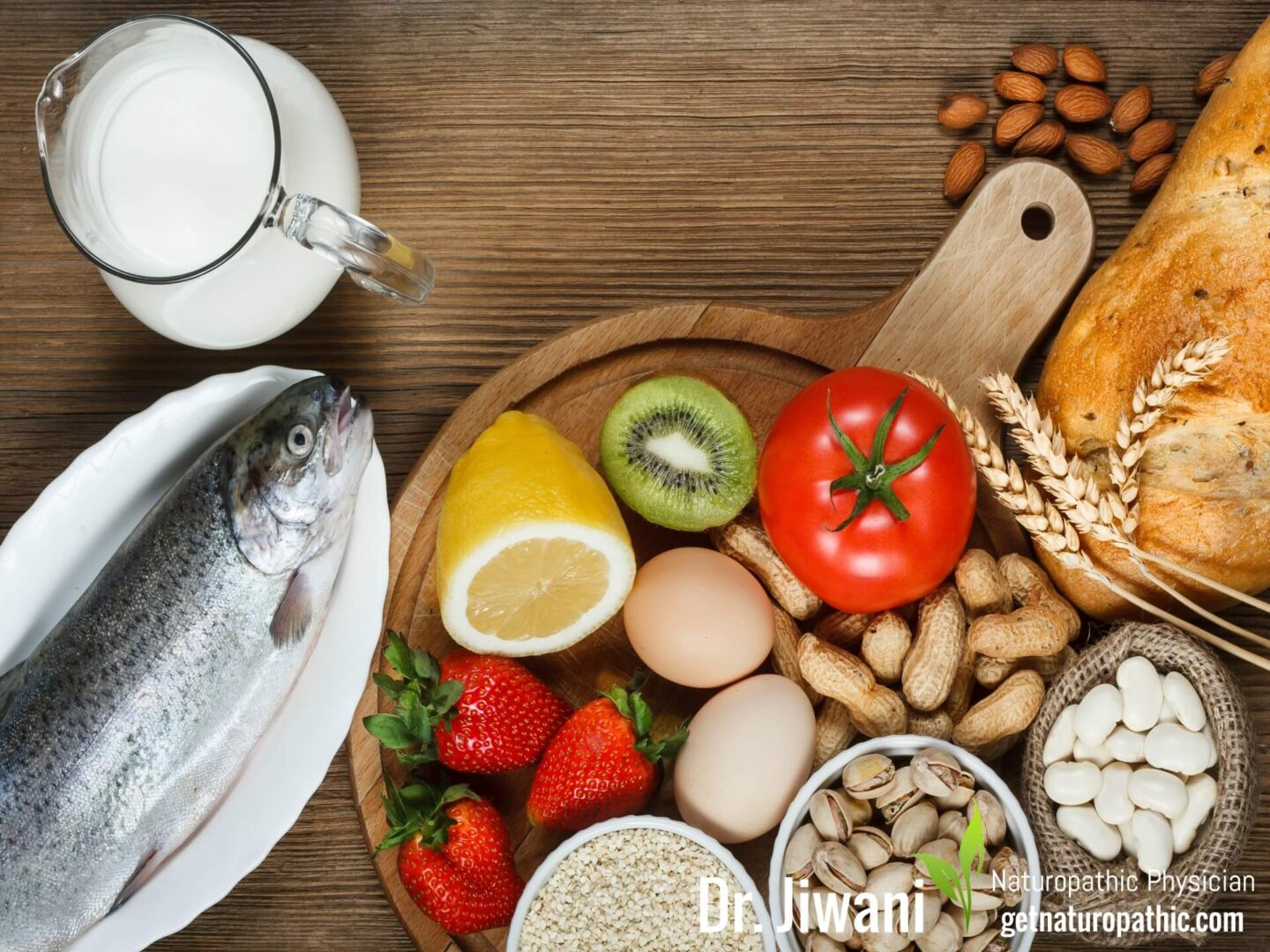
9 Surprising Symptoms Of Food Allergies
Naturopathic Nuggets about Food Allergies
- Many people have Food Allergies but don’t know it as symptoms are often vague & delayed
- Food Allergies are a sign of a defective immunity
- Food Allergies are associated with Leaky Gut Syndrome & Candidiasis (Yeast Infection in the blood)
- Symptoms of Food Allergies range from immediate, life-threatening to delayed, systemic effects causing overall poor health
- Research highlights Food Allergies as the offending culprit for many chronic conditions
- For appropriate food allergy blood testing, healthy dietary adjustments & treatment of adverse consequences, see a licensed Naturopathic Physician
Most people think that Food Allergies have a sudden, throat-closing effect. Actually, 80-90% of allergic reactions in the body are not immediate. Almost 33% of the industrialized world suffers from Allergies. Food Allergies have been self-reported by 2.5 million Canadians & 15 million Americans. Research reviews have highlighted this alarming prevalence of food allergies in 15-20% of babies (Ho et al. 2014). This makes food allergies a growing concern in our healthcare system, as they are quickly undermining our health.
Food Allergies? You’re Overreacting!
Allergies are an overreaction of a normal immune response. Your immunity is a powerful, intricate system that protects you from foreign invaders, while also repairing cancer cells. Your immunity combats bacteria, viruses & fungi that cause sickness & infection. In fact, the strength of your immunity reflects your vulnerability to infection.
Not All Allergies Are Equal
There are different types of allergic reactions. Developed or acquired allergies may occur from constantly eating the same foods. Completely avoiding the food for a time, however, may allow the immune system to forget that it’s allergic. Thereafter, occasionally eating that food may be ok. Allergies that you are born with are fixed, immediate reactions that occur whenever the food is eaten, no matter how long you’ve avoided it.
Allergies Indicate Poor Immunity
When food or environmental substances enter your body, a hyperactive immunity will cause an allergic reaction. People with allergies have hyperactive immune systems that produce exaggerated responses to something a healthy person would not react to. It is important to understand that if you have developed food allergies, it means that your immunity is not healthy.
Food Allergies Can Be Elusive
Food allergies affect many people at some point in their life. The solution to achieving optimal health lies in acknowledging the link between diet and disease. Unfortunately, conventional medicine does not support this theory. People may or may not notice when a symptom occurs after eating. Figuring out which food is the culprit becomes challenging when we consider how complex our diets are. What with processed foods having dozens of ingredients makes labels difficult to understand. Determining your food allergies becomes nearly impossible when differing allergic pathways occur causing immediate, delayed & cumulative reactions.
Food Allergies Lead To Leaky Gut Syndrome
Acquired food allergies can occur from eating the same foods, poor digestion and weakened integrity of the intestinal barrier, known as Leaky Gut Syndrome. It is now understood that poor digestion of proteins may cause large, undigested particles to escape through the leaky gut into the bloodstream. Your immunity, in turn, sees this as an attack and launches an allergic reaction. Not that the food is “bad” for you, but rather the food particles are larger than they should be. The food-allergic reaction can affect any site in the body as it occurs in the bloodstream, including skin, joints, bowels & brain. The inflammation from your food allergies can worsen Leaky Gut Syndrome creating a vicious cycle of damage. This will continue unchecked until the problematic foods are eliminated and the leaky gut is repaired.
Gut – Allergy – Yeast Connection
Leaky Gut Syndrome is scientifically termed as “increased intestinal permeability” or intestinal barrier dysfunction. This means that there is damage to the intestines as if there are holes in a sieve. The leaky gut allows larger, undigested food particles to enter your bloodstream. Toxins and unwanted microbes like yeast infiltrate also, breaking down your immunity. The systemic infection of yeast in your blood is called Candidiasis, which compromises your immunity further, leading to many chronic symptoms.
Surprising Symptoms Of Food Allergies
Most allergic reactions are the acquired type. These occur in the bloodstream rather than the mucous membranes, so the symptoms are more vague and delayed in effect. Some people suffer from symptoms that don’t affect others due to their genetics. The nine surprising symptoms associated with Food Allergies are:
1. Food Allergies Can Cause Digestive Disturbances:
Food allergies can cause many types of digestive difficulties including diarrhea, constipation, gas, bloating, heartburn, acid reflux, ulcers, canker sores & abdominal pain. These may be the cause of Leaky Gut Syndrome which is caused by your food allergies.
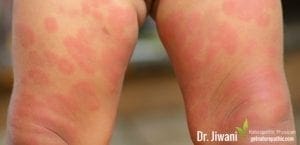
2. Food Allergies Can Cause Skin Rashes:
Inflammation in the skin occurs in many different ways. Hives (urticaria) are red, raised welts that come & go often for months to years. Eczema can arise at any age, often resulting in red, dry rash with a maddening itch. Eczema can spread over time when food allergies remain untreated. Food Allergies can trigger an autoimmune response to mistakenly attack healthy skin as Alopecia, Lupus, Psoriasis, Vitiligo, Scleroderma,& Sjogren’s Syndrome.
3. Food Allergies Can Cause Weight Gain & Water Retention:
Food allergies cause inflammation & water retention as a result of the allergic reaction. The inflammation triggers stress hormones to increase the fat storing hormone insulin. The more fat you store, the more inflammation you create which perpetuates this vicious cycle.
4. Food Allergies Can Cause Fatigue, Lethargy:
The symptom of fatigue & lethargy may be due to many reasons ultimately caused by food allergies. Malabsorption of nutrients can occur from Leaky Gut Syndrome resulting in protein, vitamin & mineral deficiencies. In turn, cellular, metabolic & hormonal processes are disrupted. This can manifest as anemia (iron deficiency), low thyroid, sleep apnea & diabetes. If you find unexplained vitamin & mineral deficiencies through conventional lab testing, you may wish to explore the potential cause: your food allergies!
5. Food Allergies Can Cause Immune Dysfunction:
Food allergies may cause various forms of immune dysfunction, depending on your genetics. Immune dysfunction can manifest as recurring infections, environmental allergies and/or autoimmunity. Autoimmunity is an abnormal immunity that self destructs. The pathway of damage of autoimmune diseases is inflammation, which results in the dysfunction & destruction of various body tissues. Autoimmune diseases can affect many parts of the body including your joints, thyroid, skin, hair, liver, kidneys, muscles, spine, stomach and lungs.
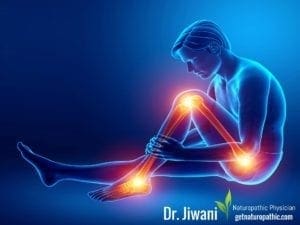
6. Food Allergies Can Cause Muscular or Joint Pains:
Food allergies affect the body through an inflammatory response which can cause pain & swelling. This effect may vary from brief, mild & temporary discomfort to chronic, severe pain and eventually destruction of the cartilage or cushion between the joints (Osteoarthritis).
7. Food Allergies Can Cause Mental & Emotional Afflictions:
Food allergies can affect the balance of many different hormones including thyroid, cortisol & serotonin. As a result, mood swings, poor sleep, anxiety, depression, food cravings, poor concentration & memory, brain fog, fatigue & hyperactivity may occur.
8. Food Allergies Can Cause Chronically Swollen Glands:
Food allergies stimulate an immune & inflammatory response. When this constantly occurs, it can lead to chronically swollen lymph nodes. This is a sign of an exhausted overworked immune system.
9. Food Allergies Can Cause Heart Symptoms:
Food allergies can cause alterations in blood flow & heart rhythms causing high blood pressure & heart palpitations.
These symptoms may occur together or individually.
Food Allergies & Your Health
Decades of research show food allergies are causative for many conditions, including:
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Autism (ASD)
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Bedwetting (Enuresis)
- Canker Sores (Apthous Ulcers)
- Chronic Fatigue
- Colitis
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Recurrent Ear Infections
- Eczema
- Fibromyalgia
- Gallbladder Disease
- Hay Fever
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Kidney Disease
- Migraines
- Psoriasis
- Thyroid Dysfunction
Not All Allergy Tests Are Created Equal
Diagnosis of food allergies can be determined using various methods and some are much better than others. Lab methods attempt to measure antibody levels whereas clinical tests challenge patients with suspected allergens and watch for reactions. Apart from the Skin Prick Test and the Vega Test (an electro-diagnostic method), there stands a state of the art technology called the ELISA test (Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay) used for Food Allergy Blood Testing. This type of technology (ELISA) is also used to diagnose Pregnancy, HIV & Hepatitis.
The Best Allergy Test
The ELISA testing procedure for food allergies may be available from some Naturopathic Physicians. It involves a blood sample drawn from the patient being tested for food allergies, on ninety-six different foods measuring two different antibodies. It is critical to ensure that the lab does duplicate testing for accurate & reproducible results. Ultimately, food allergies need to be identified and eliminated with medical supervision by a licensed Naturopathic Physician. This is essential to ensure the modified diet required is metabolically balanced, addressing nutrient deficiencies & other consequences.
The Other Part Of The Picture
It is just as important to address the following consequences of your food allergies as it is to avoid the problematic foods. The following health issues may be the result of food allergies and should be treated alongside diet modifications:
- Heal The Leaky Gut
- Improve Digestion
- Increase Probiotics (Good Guys)
- Address Parasite / Fungal Infections / Candidiasis (Bad Guys)
- Address Nutrient Deficiencies
- Support Immunity
- Support Adrenals
- Regulate Inflammation & Histamine
- Address Hormonal Imbalances
- Enhance Anti-inflammatory Pathways by:
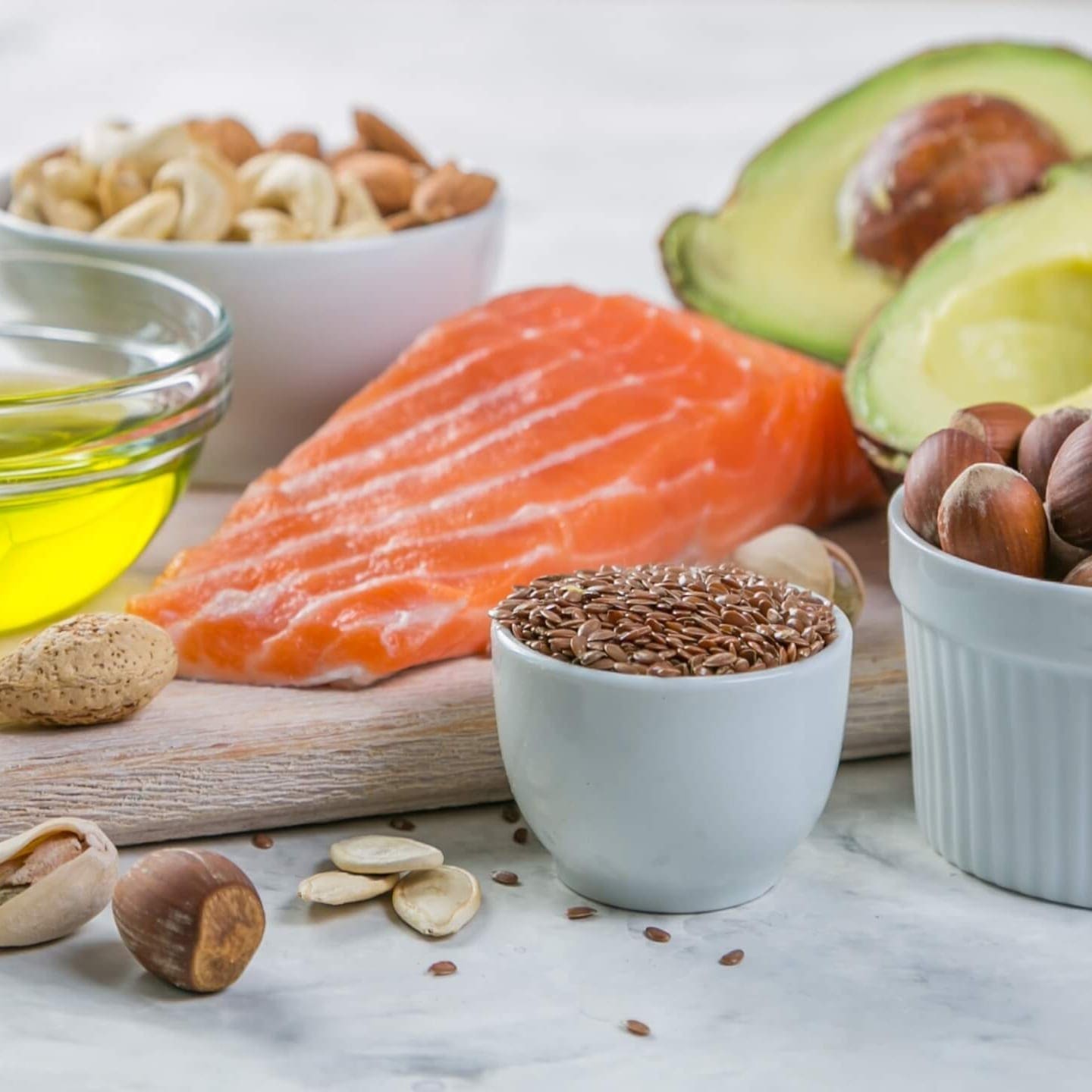
- Increasing Good Fats (Omega 3): Flax Oil, Hemp Oil, Wild Fish, Grass Fed Red Meats, Chia Seeds, Flax Seeds, Hemp Seeds, Caviar, Walnuts, Egg Yolks, Spinach
- Reduce Saturated Fats: Red Meat, Margarine, Corn Oil, Peanut Oil, Soybean Oil, Vegetable Oil
The Final Word
Food allergies are a rapidly growing health concern affecting the majority of our society. Given the systemic, delayed nature of most allergic reactions, you may not realize that you have food allergies. As with any health concern, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a licensed Naturopathic Physician for proper testing, planning & avoidance. A multi-faceted approach is necessary to ensure not only alleviation of your allergic symptoms, but an enhanced functioning of every system to ensure optimal health.
Related Leaky Gut Syndrome: Science, Symptoms & Solutions
References
Abdel-Hafez M, Shimada M, Lee PY, Johnson RJ, Garin EH. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and atopy: is there a common link?. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2009 Nov 30;54(5):945-53.
Alpay K, Ertaş M, Orhan EK, Üstay DK, Lieners C, Baykan B. Diet restriction in migraine, based on IgG against foods: A clinical double-blind, randomised, cross-over trial. Cephalalgia. 2010 Jul;30(7):829.
Aydoğan B, Kiroğlu M, Altintas D, Yilmaz M, Yorgancilar E, Tuncer Ü. The role of food allergy in otitis media with effusion. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 2004 Jun;130(6):747-50.
Cai M, Zeng L, Li LJ, Mo LH, Xie RD, Feng BS, Zheng PY, Liu ZG, Liu ZJ, Yang PC. Specific immunotherapy ameliorates ulcerative colitis. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 2016 Aug 5;12(1):37.
Czkwianianc E, Raczyński P, Kubińska I, Ryszard M, Alina D, Ewa MP. The occurrence of gallbladder contractility disorders in children with some diseases presenting as abdominal pain. Polski merkuriusz lekarski: organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego. 2009 May;26(155):420-4.
Gaby AR. The role of hidden food allergy/intolerance in chronic disease. Alternative Medicine Review. 1998 Apr;3:90-100.
Goebel A, Buhner S, Schedel R, Lochs H, Sprotte G. Altered intestinal permeability in patients with primary fibromyalgia and in patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Rheumatology. 2008 Aug 1;47(8):1223-7.
Hafström I, Ringertz B, Spångberg A, Von Zweigbergk L, Brannemark S, Nylander I, Rönnelid J, Laasonen L, Klareskog L. A vegan diet free of gluten improves the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: the effects on arthritis correlate with a reduction in antibodies to food antigens. Rheumatology. 2001 Oct 1;40(10):1175-9.
Ho MH, Wong WH, Chang C. Clinical spectrum of food allergies: a comprehensive review. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology. 2014 Jun 1;46(3):225-40.
Katta R, Schlichte M. Diet and dermatitis: food triggers. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. 2014 Mar;7(3):30.
Levy Y, Segal N, Weintrob N, Danon YL. Chronic urticaria: association with thyroid autoimmunity. Archives of disease in childhood. 2003 Jun 1;88(6):517-9.Morton S, Palmer B, Muir K, Powell RJ. IgE and non-IgE mediated allergic disorders in systemic lupus erythematosus. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 1998 Nov 1;57(11):660-3.
Lindqvist U, Rudsander Å, Boström Å, Nilsson B, Michaelsson G. IgA antibodies to gliadin and coeliac disease in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology. 2002 Jan 1;41(1):31-7.
Morton S, Palmer B, Muir K, Powell RJ. IgE and non-IgE mediated allergic disorders in systemic lupus erythematosus. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 1998 Nov 1;57(11):660-3.
Nanda R, James R, Smith H, Dudley CR, Jewell DP. Food intolerance and the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1989 Aug 1;30(8):1099-104.
Nigg JT, Holton K. Restriction and elimination diets in ADHD treatment. Child and adolescent psychiatric clinics of North America. 2014 Oct 31;23(4):937-53.
Nolan A, Lamey PJ, Milligan KA, Forsyth A. Recurrent aphthous ulceration and food sensitivity. Journal of oral pathology & medicine. 1991 Nov 1;20(10):473-5.
Platts-Mills TA. The role of immunoglobulin E in allergy and asthma. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2001 Oct 15;164(supplement_1):S1-5.
Schnoll R, Burshteyn D, Cea-Aravena J. Nutrition in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a neglected but important aspect. Applied Psychophysiology and biofeedback. 2003 Mar 1;28(1):63-75.
Straus SE, Dale JK, Wright R, Metcalfe DD. Allergy and the chronic fatigue syndrome. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1988 May 31;81(5):791-5.
Theoharides TC, Zhang B. Neuro-inflammation, blood-brain barrier, seizures and autism. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2011 Nov 30;8(1):168.
Waserman S, Watson W. Food allergy. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 2011 Nov 10;7(1):S7.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not advocate self-diagnosis. Due to individual variability, consultation with a licensed health professional, such as a licensed naturopathic physician is highly recommended, prior to starting a natural treatment plan. For further information, see Terms of our Website.
Follow Dr. Jiwani
Popular Posts